Extensible Firmware Interface Specification
17-10 12/01/02 Version 1.10
17.3.2.1 Data Structures
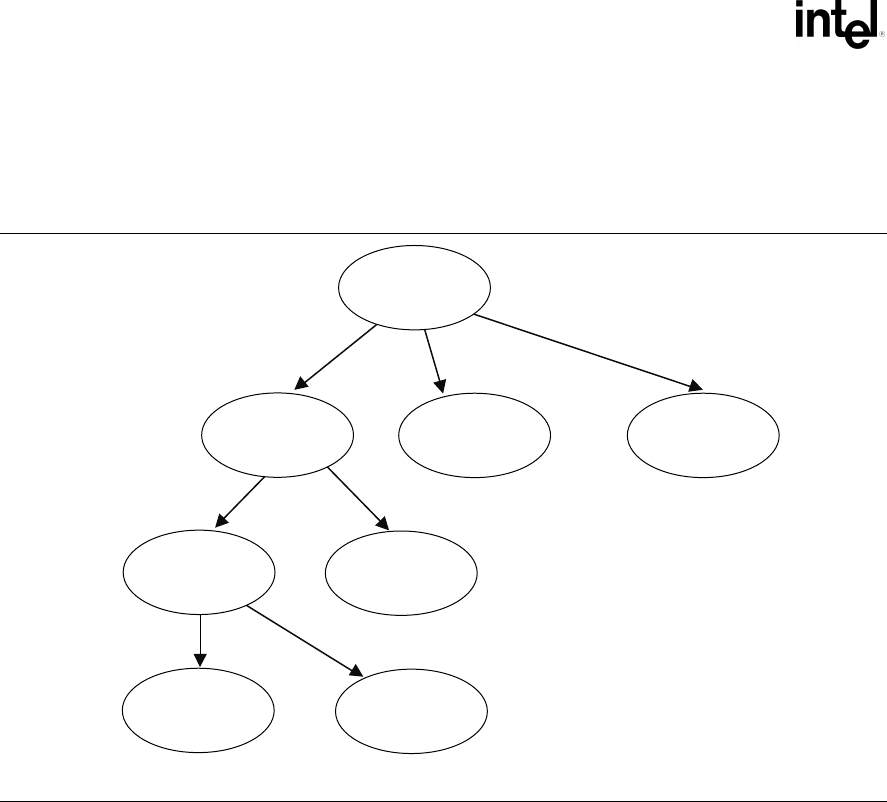
The String Info Log is implemented as a set of search trees. These search trees are dynamically
updated as the compression proceeds through the source data. The structure of a typical search tree
is depicted in Figure 17-5.
1
Char: "c"
"a"
"m" "q"
2
34
Level: 3
Pos: 500
Pos: 500
Pos: 600
Pos: 500
Level: 8
Pos: 400
Pos: 400 Pos: 350
5
6
7
8
"x"
"k"
"p"
"t"
OM13177
Figure 17-5. String Info Log Search Tree
There are three types of nodes in a search tree: the root node, internal nodes, and leaves. The root
node has a “character” attribute, which represents the starting character of a string. Each edge also
has a “character” attribute, which represents the next character in the string. Each internal node has
a “level” attribute, which indicates the character on any edge that leads to its child nodes is the
“level + 1”th character in the string. Each internal node or leaf has a “position” attribute that
indicates the string’s starting position in the source data.
To speed up the tree searching, a hash function is used. Given the parent node and the edge-
character, the hash function will quickly find the expected child node.


















