iMac (24-inch Mid 2007) Take Apart — Symptom Charts 217
Display Panel
Black and white splotches on the LCD panel after it runs for awhile
Check the hard drive. The hard drive should be mounted with the circuit board facing up or
out towards the LCD as shown in the hard drive chapter. It’s possible to mount the hard drive
upside down (hard drive top cover facing LCD) which generates a corrupted image (black and
white splotches) on the LCD panel after it runs a while.
Display does not change but the mouse still moves
Make sure all software updates have been applied to the computer. Refer to KBase article
303903, Intel-based iMac: Installing available updates , and to Apple Downloads for all
available updates for the iMac (Mid 2007) model of computers
When displaying a single color over the screen area, the LCD panel shows one or
more pixels that are not properly lit.
Active-matrix LCD technology uses rows and columns of addressable locations (pixels) that
render text and images on screen. Each pixel location has three separate subpixels (red, green,
and blue) that allow the image to be rendered in full color. Each subpixel has a corresponding
transistor responsible for turning the subpixel on or o.
There are typically millions of these subpixels on an LCD display. For example, the LCD panel used
in the Apple Cinema HD display is made up of 2.3 million pixels and 6.9 million red, green, and
blue subpixels. Occasionally, a transistor does not work perfectly, which may result in the aected
subpixel being turned on (bright) or turned o (dark). With the millions of subpixels on a display,
it is quite possible to have a low number of faulty transistors on an LCD. Therefore, a certain
number of subpixel anomalies is considered acceptable. Rejecting all but perfect LCD panels
would signicantly increase the retail price for products using LCD displays. These factors apply
to all manufacturers using LCD technology—not just Apple products.
To determine whether or not the display has an acceptable number of pixel anomalies, follow the
steps below:
Set the display image to one of the following colors: all-white display, all-red display, all-green 1.
display, or all-blue display.
Using a jeweler’s loupe, pocket microscope, or other magnifying device, identify and count 2.
each subpixel anomaly:
• Bright subpixel anomaly = subpixel that is always on
• Dark subpixel anomaly = subpixel that is always o
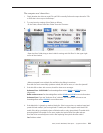
Important: 3. Check the number of subpixel anomalies with the following chart:
LCD Size
(inches)
Acceptable Number of Subpixel
Anomalies
Replace the Display
Bright Dark Both Bright Dark Both