40930701TH DRAFT Vesion 18 /
(a) Centronics bidirectional parallel interface
This is an interface conforming to IEEE-1284 and provides either of unidirectional and
bidirectional communications according to each of the following communication modes.
• Compatibility mode
Unidirectional communications from the host to the printer.
• Nibble mode
This mode transmits 4-bit wide data from the printer to the host. In this mode, each
1-byte data is transferred in the form of two nibbles using ERROR, BUSY, FAULT,
and SELECT signal leads. This mode can provide the bidirectional operation in
combination with the compatibility mode.
• ECP mode
This mode provides the asynchronous bidirectional interface and transmits and
receives 1-byte data using eight data signal leads under the semi-duplex control by
the host.
When the power is turned on, the compatibility mode is automatically selected. The
change to another mode from the compatibility mode is made through negotiation.
(When the BI DIRECTION is set to ENABLE in the menu, this change can be performed.)
(For the electrical/physical characteristics of this interface, see APPENDIX B)
(b) RS232C serial interface
The following protocol is supported for the serial interface conforming to EIA RS232C.
• READY/BUSY (DTR HI or DTR LO)
• X-ON/X-OFF
• RBST X-ON
(For the electrical/ physical characteristics of the interface, see APPENDIX B)
(c) OKI HSP interface (Option)
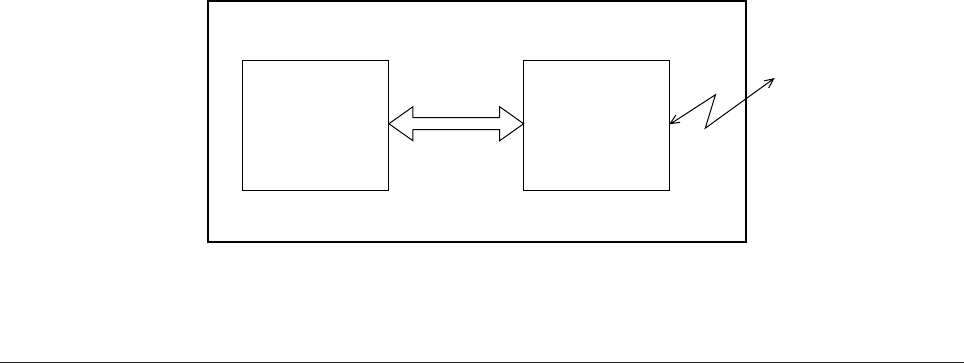
This interface (slot) is an OKI unique universal interface that provides the platform to
connect various of boards (including those supplied by third venders) such as the LAN
connection expansion board and SCSI expansion board.
Any expansion boards compatible with this interface can be mounted on the Control
board in the piggyback board from without modifying the program at the printer side. The
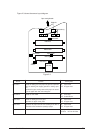
conceptual diagram of the OKI HSP interface is shown in Figure 2-2.
(For the electrical/physical characteristics of the OKI HSP interface, see the OKI HSP
interface technical manual.)
Printer
Control board
LAN
expansion board
OKI HSP
interface
Network, etc.
Figure 2-2