2-48 IBM Informix OnLine Database Server Administrator’s Guide
Shared-Memory Internal Tables
The header also contains the OnLine “magic number,” which is used to
synchronize user processes. Each OnLine releaseis assigned a magic number.
In addition, the same magic number is contained within the user process
code. Whenever a user process attempts to attach to shared memory, these
magic numbers are compared. If they are notcompatible, an error is returned.
The magic-number check ensures that the database server processes are
compatible.
Shared-Memory Internal Tables
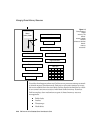
OnLine shared memory contains nine internal tables that track shared-
memory resources. (Refer to Figure 2-5 on page 2-40.) Three of these nine
tables are paired with hash tables. Each of the nine is described next.
OnLine Buffer Table
The buffer header table tracks the address and status of the individual buffers
in the shared-memory pool. When a buffer is used, it contains an image of a
data or index page from disk.
The buffer header table contains the following control information, which is
needed for buffer management:
■ Buffer status
Buffer status is described as empty, unmodified, or modified. An
unmodified buffer contains data, but this data can be overwritten. A
modified, or dirty, buffer contains data that must be written to disk
before it can be overwritten.
■ User processes currently accessing the buffer
The list of user processes is stored as a bit map. Each user sharing the
buffer accounts for one of the bits set in the bit map and increments
the buffer’s shared-user count, which is stored separately.
■ Current lock-access level
Buffers receive lock-access levels depending on the type of operation
the user process is executing. OnLine supports three buffer lock-
access levels: shared, promotable (update), and exclusive.