AI296 Version 9.8x User’s Guide
TID Multiplexing: Overview
7-2
Overview
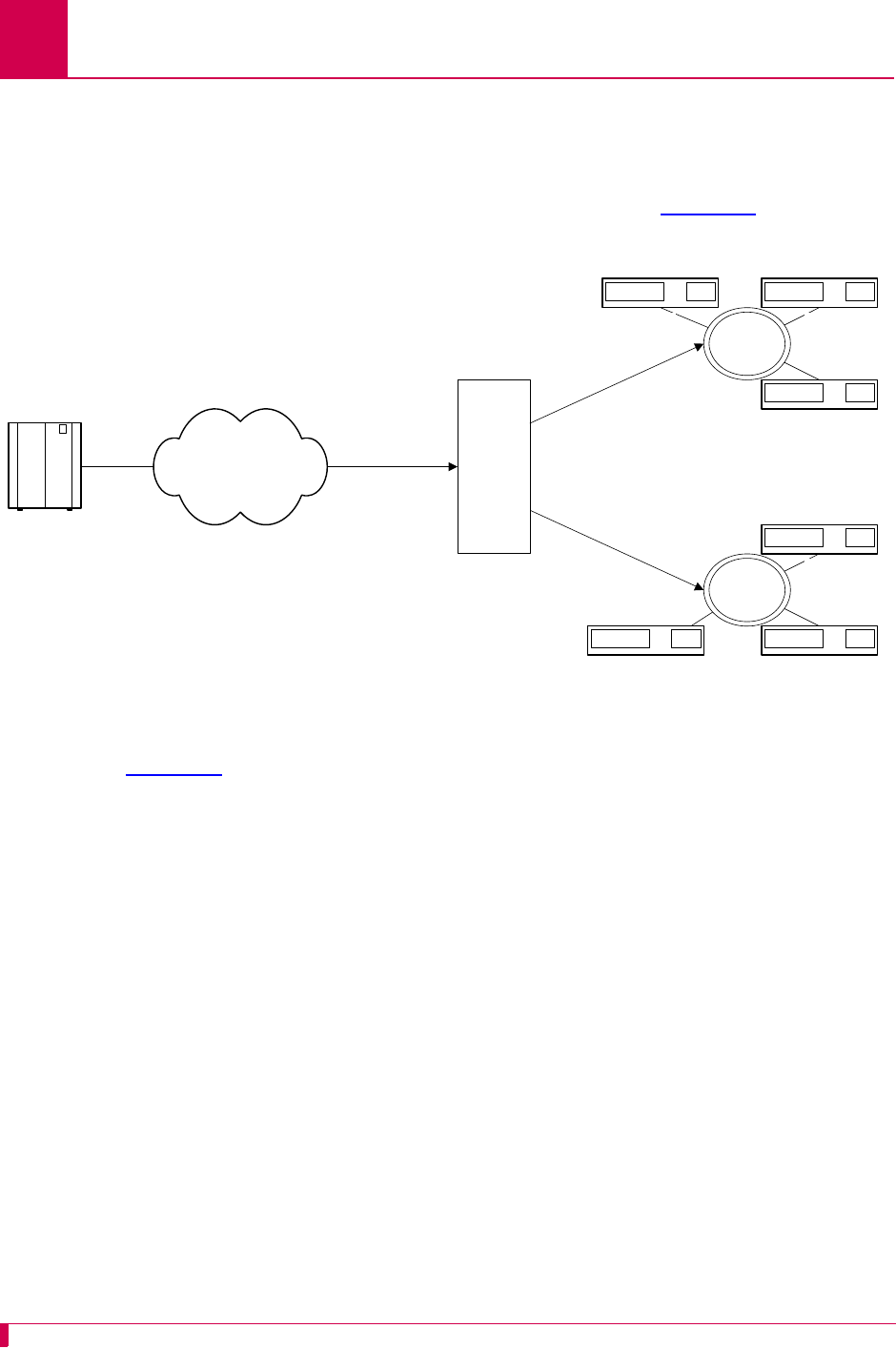
AI296 supports TID multiplexing, which enables a single call from an OSS to fan out
into multiple calls to various NEs. The initiating call may be X.25, asynchronous, or
TCP, but cannot originate from a destination menu. Refer to Figure 7-1
for an
illustration of TID multiplexing.
Figure 7-1 TID Multiplexing Overview
In Figure 7-1
, AI296 takes a single call from an OSS and routes TL1 commands to
various NEs by means of the TID in the TL1 command. Similarly, AI296 receives TL1
responses and NE reporting messages from several NEs and routes these messages
to the appropriate OSS. The call to AI296 from the OSS is a parent call. The calls
from AI296 to the various NEs are children calls.
After receiving a TL1 command from the OSS, AI296 checks to see if there is an
existing connection for each TID. If a connection to the appropriate NE is already
established, then AI296 forwards the TL1 command to the NE as specified by the TID.
The following characteristics apply to AI296 when it attempts to connect to an NE:
z If AI296 is unable to establish a connection to an NE, it will buffer the TL1
command and try to reconnect within 2 seconds.
z AI296 tries to connect up to three times if it cannot immediately establish a
connection.
z AI296 buffers only one TL1 command for each NE. If a connection is made, AI296
forwards the buffered command to the NE.
Sonet NEs
TID4
TID5TID6
Sonet NEs
X.25 Packet Switched
Network
OSS
TID2
TID3
AI296
TID1
TID1
TID2
TID3
TID4
TID5
TID6
TID1
TID2
TID3
TID4
TID5
TID6


















