6-318
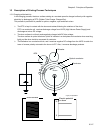
1.3.2 Exposure
In the exposure process, the drum surface charged negatively is scanned by laser beams to form invisible
electrostatic latent image on the drum surface.
This process is performed in parallel for yellow, magenta, cyan and black colors.
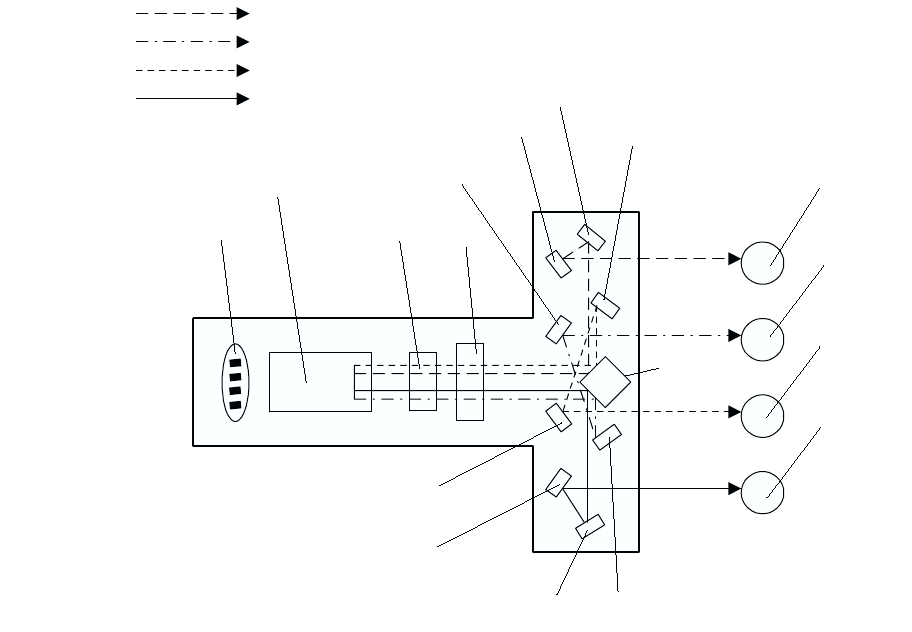
✧ Laser beams are emitted from the laser diode in the ROS ASSY. By the rotating polygon mirror, fixed
mirror and lens attached to the scanner ASSY of the ROS ASSY, each color of drum surface is
scanned from end to end in the axial direction.
✧ The laser beams are emitted based on the print data (image data) from the printer controller. When
the print data instructs to print pixel points, laser beams are generated and when the print data
instructs not to print, no laser beams are generated. (On the areas which are developed by toner, the
laser beams light up and areas which are not developed by toner, laser beams go out.)
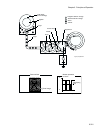
The laser beams emitted on the drum surface generate a pair (electron <=> hole) in the optical
conductive layer. [Electrons are excited on the conductive zone, causing holes at the valence band.]
Electrons are induced by the electric field, moved toward the inside metallic part and flow into it. The
holes move toward the outer surface of the optical conductive layer, are combined with the minus
charge (electron) on the outer surface again and decrease negative charge. As a result, on the drum
surface where the electric potential increases, invisible static latent image (print image) is generated.
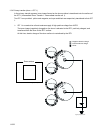
engine principle0007FA
Quad Beam Laser Diode
Polygon Mirror
Lens
Lens
Mirror
Mirror
Mirror
Mirror
Mirror
Mirror
Mirror
Mirror
Mirror
Drum (Y)
Drum (M)
Drum (C)
Drum (K)
: Laser beams (M)
: Laser beams (Y)
: Laser beams (C)
: Laser beams (K)