C
ONFIGURING
THE
S
WITCH
3-310
• By default, a stub can only pass traffic to other areas in the autonomous
system via the default external route. However, you also can configure
an area border router to send Type 3 summary link advertisements into
the stub.
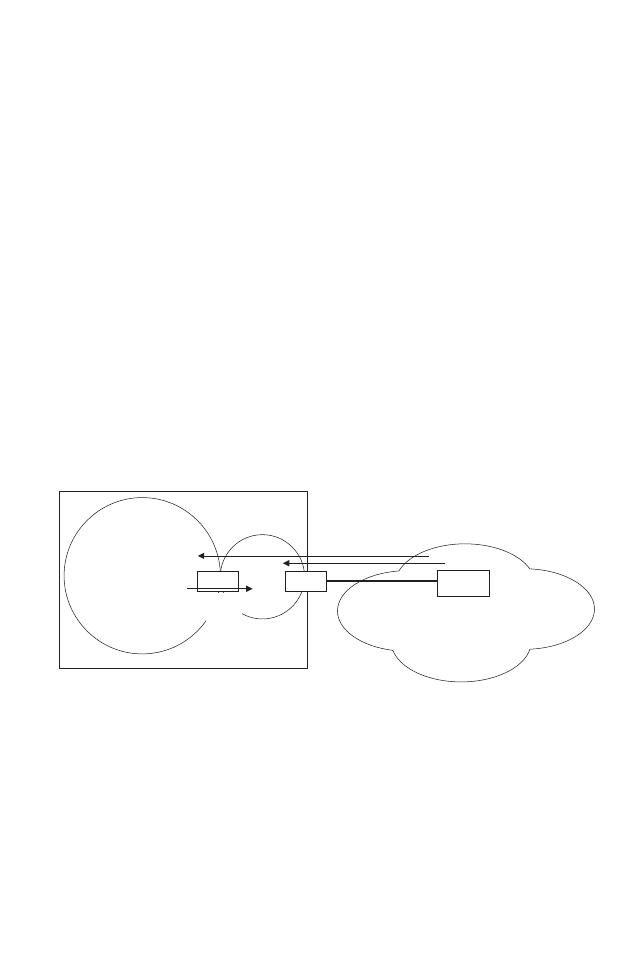
NSSA – A not-so-stubby area (NSSA) is similar to a stub. It blocks most
external routing information, and can be configured to advertise a single
default route for traffic passing between the NSSA and other areas within
the autonomous system (AS). However, an NSSA can also import external
routes from one or more small routing domains that are not part of the
AS, such as a RIP domain or locally configured static routes. This external
AS routing information is generated by the NSSA’s ASBR and advertised
only within the NSSA. By default, these routes are not flooded onto the
backbone or into any other area by area border routers. However, the
NSSA’s ABRs will convert NSSA external LSAs (Type 7) into external
LSAs (Type-5) which are propagated into other areas within the AS.
• Routes that can be advertised with NSSA external LSAs include network
destinations outside the AS learned via OSPF, the default route, static
routes, routes derived from other routing protocols such as RIP, or
directly connected networks that are not running OSPF.
• Also, note that unlike stub areas, all Type-3 summary LSAs are always
imported into NSSAs to ensure that internal routes are always chosen
over Type-7 NSSA external routes.
Default Cost – This specifies a cost for the default summary route sent into
a stub or not-so-stubby area (NSSA) from an Area Border Router (ABR).
backbone
NSSA
ABR
default external
route for localAS
ASBR
external network
Router
default external
route for another
routing domain
7
5
AS


















