Configuring PIM-DM 131
as a redundancy packet without the multicast forwarding. The unicast routing
information as path judgment can come from any unicast routing protocol
independent of any specified unicast routing protocol such as the routing
information learned by RIP.
■ Assert mechanism
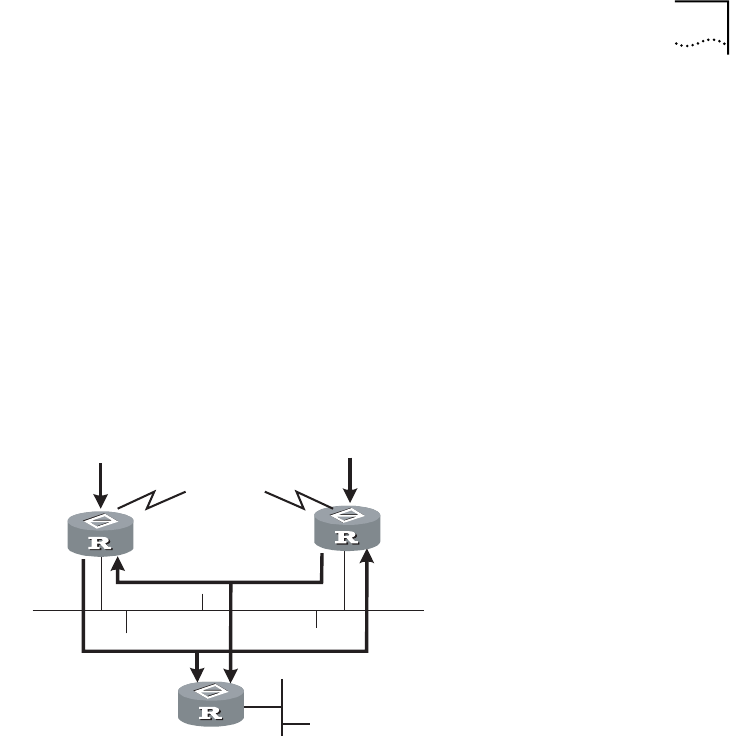
As shown in the following figure, both routers A and B on the LAN have their
own receiving paths to multicast source S. In this case, when they receive a
multicast packet sent from multicast source S, they will both forward the
packet to the LAN. Multicast Router C at the downstream node will receive two
copies of the same multicast packet.
Figure 32 Assert Mechanism Diagram
When they detect such a case, routers need to select a unique sender by using
the assert mechanism. Routers send Assert packets to select the best path. If
two or more have the same priority and metric, the path with a higher IP
address will be the upstream neighbor of the (S, G) entry. This is responsible for
forwarding the (S, G) multicast packet.
■ Graft
When the pruned downstream node needs to be restored to the forwarding
state, the node will send a graft packet to inform the upstream node.
Configuring PIM-DM is described in the following sections:
■ Configuring PIM-DM
■ Example: PIM-DM Configuration
Configuring PIM-DM Basic PIM-DM configuration includes:
■ Enabling Multicast
■ Enabling PIM-DM
■ Entering PIM View
Advanced PIM-DM configuration includes:
■ Configuring the Interface Hello Message Interval
■ Configuring the Filtering of Multicast Source/Group
■ Configuring the Filtering of PIM Neighbors
Multicast packets forwarded
by the upstream node
R
outer A
Router B
Receiver
Router C