Operation Verification Measurements
5-82 MS278XB OM
10. On the MS2781B, set Peak to CF and then set Peak to Reference Level.
11. Set the MS2781B to Single Sweep mode, press the Sweep button, and then wait for the 200 sweeps
to complete.
12. Turn on Marker 1 and Marker 2. Make Marker 2 as delta marker referenced to Marker 1.
13. Move Marker 2 to the first offset frequency from the carrier frequency. Record the marker reading
in the measured dBc column.
14. Calculate the normalized phase noise using the formula in the Calculated Phase Noise column.
Verify that the calculated value is within specification.
15. On the MS2781B, set Span and RBW to the next set of values in Table 5-7.
16. Press the Sweep button to initiate a sweep.
17. Move Marker 2 to the next offset frequency. Record the delta marker reading in the Measured
Carrier to Noise Ratio column.
18. Calculate the phase noise and verify that the value is within specification.
19. Repeat steps 15 through 18 for the rest of the offset frequencies listed in Table 5-7.
20. Turn off Marker 2.
21. Record the Marker 1 power as the Measured Carrier Power in Table 5-8.
(Use this to compute the Measured Carrier to Noise Ratio in Step 24.)
22. For frequency offsets
≥1 MHz, set the MS2781B as follows:
a. Frequency Span: 1 kHz
b. Reference Level: –25 dBm
c. RBW: 10 kHz
d. VBW: Auto
e. Sweep Time: 120 Seconds
f. Attenuation: 0 dB
g. Trace Mode: Clear-Write
h. Detector: RMS
i. Optimize Phase Noise: Manual
j. Optimize Phase Noise Offset: >85 kHz
23. Set the Center Frequency as indicated in Table 5-8 and initiate a sweep.
24. After the sweep passes Marker 1, record the difference between the marker value and the
Measured Carrier Power as the Measured Carrier to Noise Ratio in Table 5-8.
25. Repeat Step 23 and Step 24 for the rest of the Center Frequencies listed in Table 5-8.
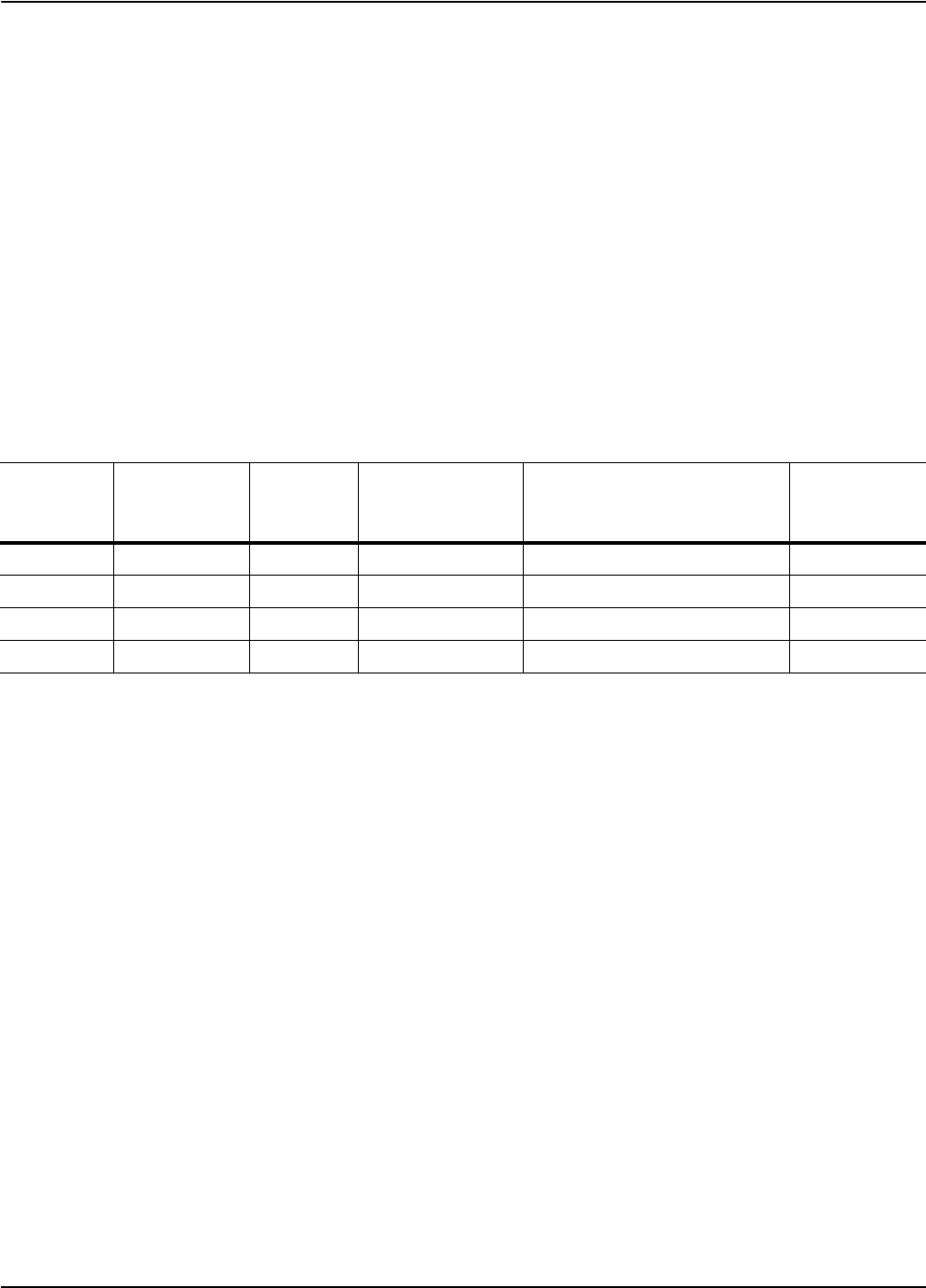
Table 5-7. Single Sideband Phase Noise Test
Offset Span RBW
Measured Carrier
to Noise Ratio
C/N (dBc)
Calculated Phase Noise
(dBc/Hz)
Specification
(dBc/Hz)
100 Hz 250 Hz 10 Hz C/N–10 dB=
< –90
1 kHz 2.5 kHz 100 Hz C/N–20 dB=
< –109
10 kHz 25 kHz 1 kHz C/N–30 dB=
< –116
100 kHz 250 kHz 10 kHz C/N–40 dB=
< –116