35-12
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using ASDM
Chapter 35 Configuring NAT (ASA 8.2 and Earlier)
NAT Overview
For policy static NAT, both translated and remote hosts can originate traffic. For traffic originated on the
translated network, the NAT rule specifies the real addresses and the destination addresses, but for traffic
originated on the remote network, the rule identifies the real addresses and the source addresses of
remote hosts who are allowed to connect to the host using this translation.
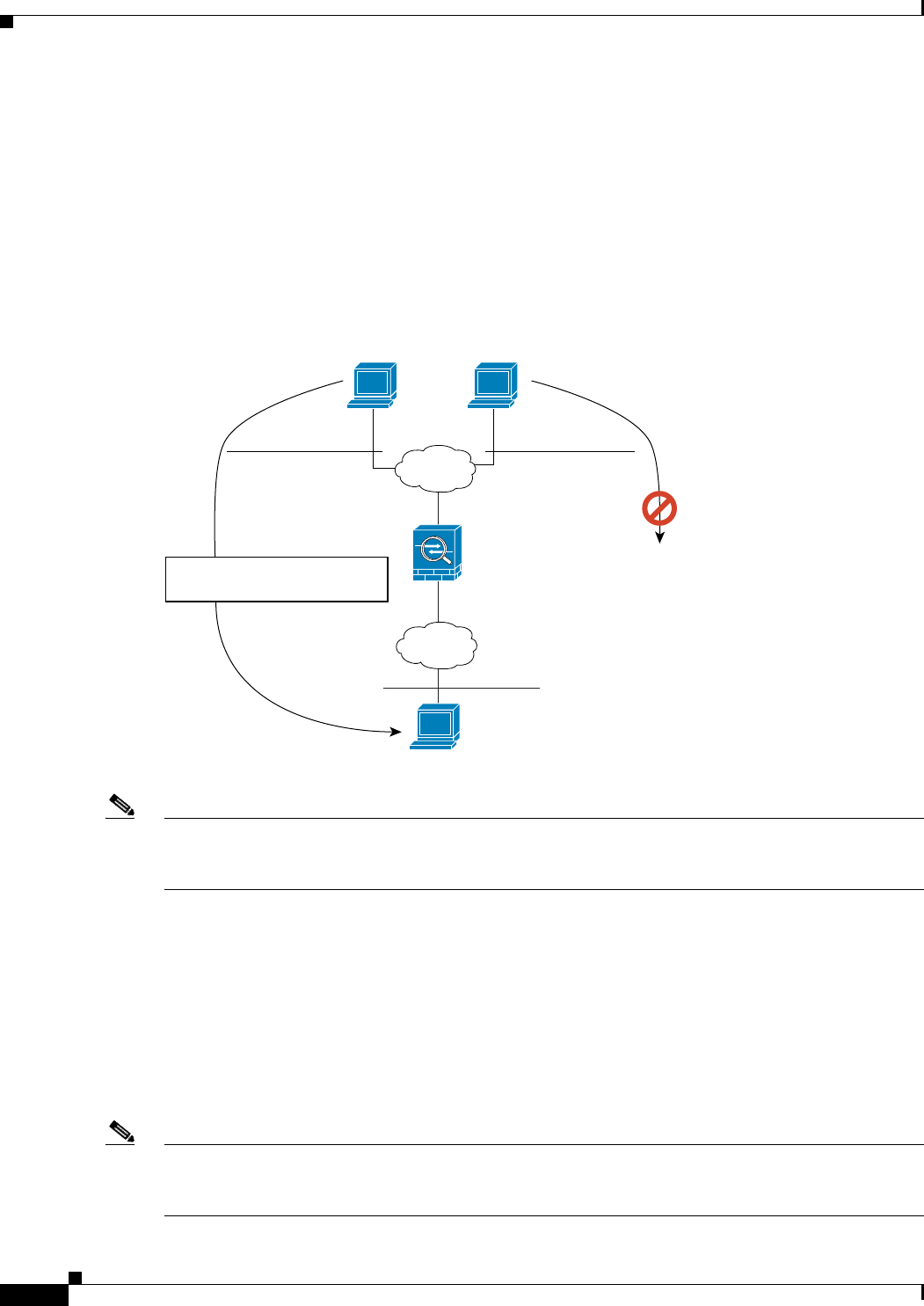
Figure 35-11 shows a remote host connecting to a translated host. The translated host has a policy static
NAT translation that translates the real address only for traffic to and from the 209.165.201.0/27
network. A translation does not exist for the 209.165.200.224/27 network, so the translated host cannot
connect to that network, nor can a host on that network connect to the translated host.
Figure 35-11 Policy Static NAT with Destination Address Translation
Note Policy NAT does not support SQL*Net, but it is supported by regular NAT. See the “When to Use
Application Protocol Inspection” section on page 46-2 for information about NAT support for other
protocols.
NAT and Same Security Level Interfaces
NAT is not required between same security level interfaces even if you enable NAT control. You can
optionally configure NAT if desired. However, if you configure dynamic NAT when NAT control is
enabled, then NAT is required. See the “NAT Control” section on page 35-4 for more information. Also,
when you specify a group of IP address(es) for dynamic NAT or PAT on a same security interface, then
you must perform NAT on that group of addresses when they access any lower or same security level
interface (even when NAT control is not enabled). Traffic identified for static NAT is not affected.
Note The ASA does not support VoIP inspection engines when you configure NAT on same security
interfaces. These inspection engines include Skinny, SIP, and H.323. See the “When to Use Application
Protocol Inspection” section on page 46-2 for supported inspection engines.
209.165.201.11 209.165.200.225
DMZ
Inside
No Translation
10.1.2.27
10.1.2.27
10.1.2.0/27
209.165.201.0/27 209.165.200.224/27
Undo Translation
209.165.202.128
130037


















