14-9
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using ASDM
Chapter 14 Completing Interface Configuration (Routed Mode)
Completing Interface Configuration in Routed Mode
d. (Optional) To assign an administrative distance to the learned route, enter a value between 1 and
255 in the DHCP Learned Route Metric field. If this field is left blank, the administrative
distance for the learned routes is 1.
e. (Optional) To enable tracking for DHCP-learned routes, check Enable Tracking for DHCP
Learned Routes. Set the following values:
Track ID—A unique identifier for the route tracking process. Valid values are from 1 to 500.
Track IP Address—Enter the IP address of the target being tracked. Typically, this would be the
IP address of the next hop gateway for the route, but it could be any network object available
off of that interface.
Note Route tracking is only available in single, routed mode.
SLA ID—A unique identifier for the SLA monitoring process. Valid values are from 1 to
2147483647.
Monitor Options—Click this button to open the Route Monitoring Options dialog box. In the
Route Monitoring Options dialog box you can configure the parameters of the tracked object
monitoring process.
f. (Optional) To set the broadcast flag to 1 in the DHCP packet header when the DHCP client sends
a discover requesting an IP address, check Enable DHCP Broadcast flag for DHCP request
and discover messages.
The DHCP server listens to this broadcast flag and broadcasts the reply packet if the flag is set
to 1.
g. (Optional) To renew the lease, click Renew DHCP Lease.
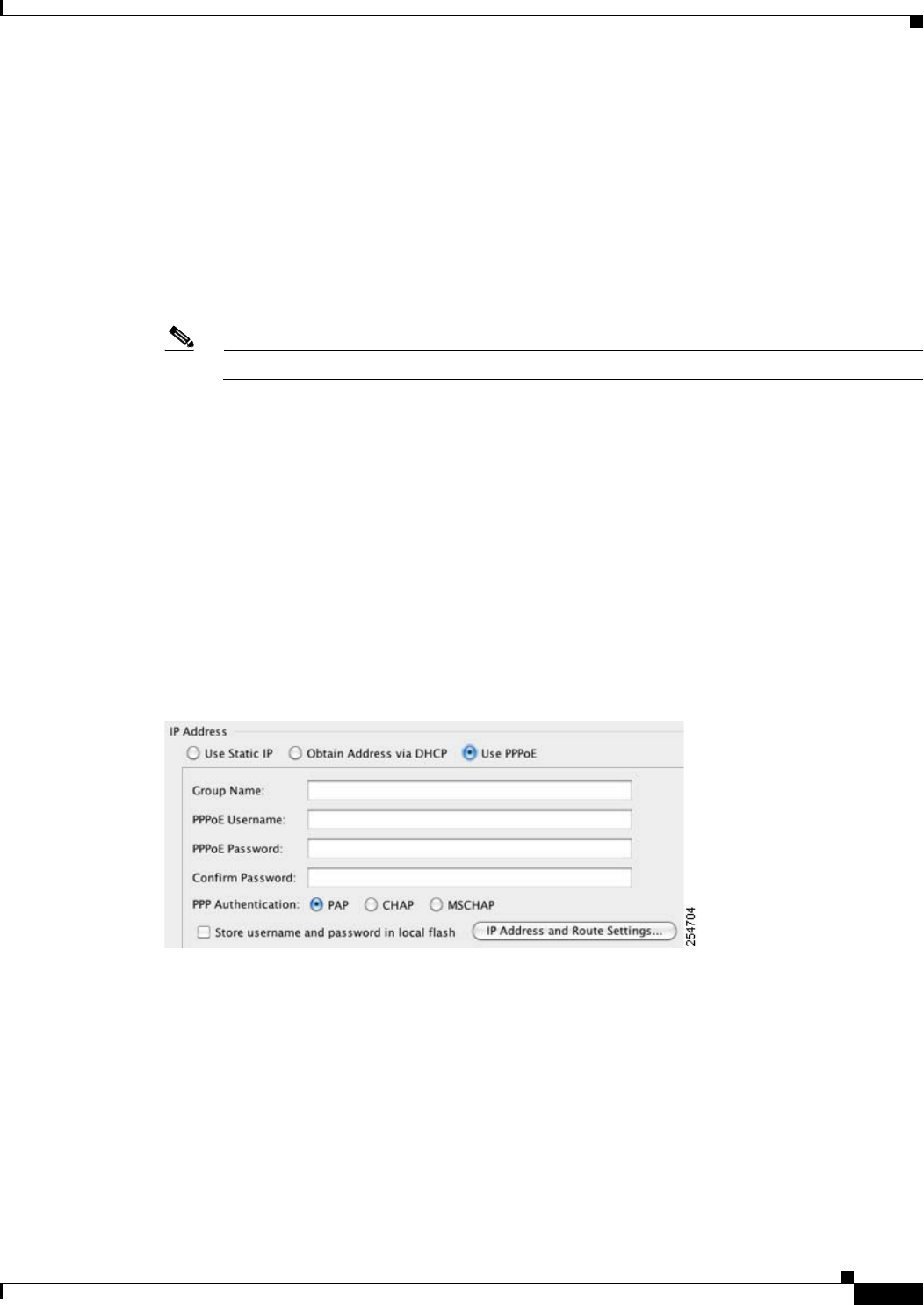
• (Single mode only) To obtain an IP address using PPPoE, check Use PPPoE.
a. In the Group Name field, specify a group name.
b. In the PPPoE Username field, specify the username provided by your ISP.
c. In the PPPoE Password field, specify the password provided by your ISP.
d. In the Confirm Password field, retype the password.
e. For PPP authentication, click either the PAP, CHAP, or MSCHAP radio button.
PAP passes cleartext username and password during authentication and is not secure. With
CHAP, the client returns the encrypted [challenge plus password], with a cleartext username in
response to the server challenge. CHAP is more secure than PAP, but it does not encrypt data.


















