Chapter 4. Virtualization concepts 77
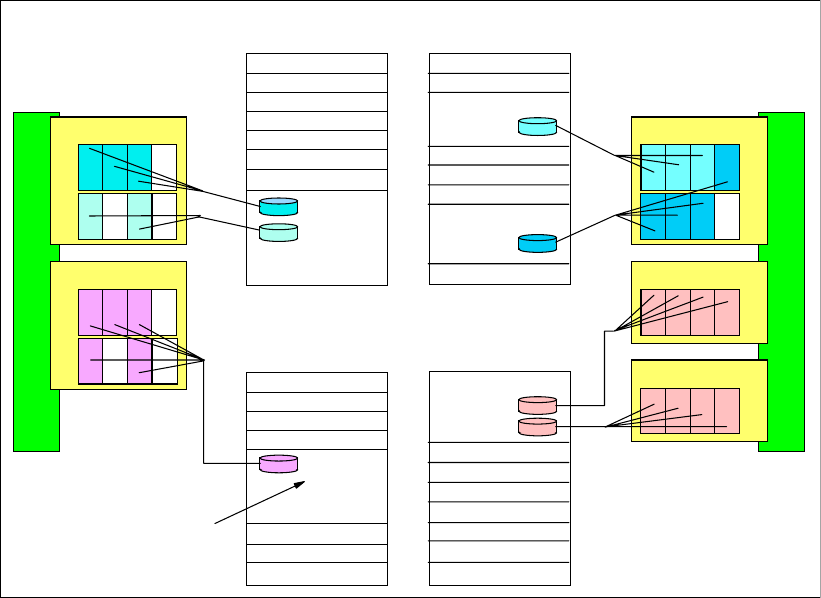
4.2.7 Address groups
Address groups are created automatically when the first LSS associated with the address
group is created and deleted automatically when the last LSS in the address group is deleted.
LSSs are either CKD LSSs or FB LSSs. All devices in an LSS must be either CKD
or FB. This
restriction goes even further. LSSs are grouped into address groups of 16 LSSs. LSSs are
numbered X'ab', where a is the address group and b denotes an LSS within the address
group. So, for example, X'10' to X'1F' are LSSs in address group 1.
All LSSs within one address group have to be of the same type, CKD or FB. The first LSS
defined in an address group fixes the type of that address group.
Figure 4-9 illustrates the concept of LSSs and address groups.
Figure 4-9 Logical subsystems
The LUN identifications X'gabb' are composed of the address group X'g', and the LSS
number within the address group X'a', and the position of the LUN within the LSS X'bb'. For
example LUN X'1101' denotes the second (X'01') LUN in LSS X'11' of address group 1.
4.2.8 Volume access
A DS6000 provides mechanisms to control host access to LUNs. In most cases a server has
two or more HBAs and the server needs access to a group of LUNs. For easy management of
server access to logical volumes, the DS6000 introduced the concept of host attachments
and volume groups.
Address group X'1x': FB
Address group X'0x' CKD
Extent Pool FB-2
LSS X'00'
LSS X'02'
LSS X'04'
LSS X'06'
LSS X'08'
LSS X'0A'
LSS X'0C'
LSS X'0E'
LSS X'10'
LSS X'12'
LSS X'14'
LSS X'16'
LSS X'18'
LSS X'1A'
LSS X'1C'
LSS X'1E'
LSS X'01'
LSS X'03'
LSS X'05'
LSS X'07'
LSS X'09'
LSS X'0B'
LSS X'0D'
LSS X'11'
LSS X'0F'
LSS X'13'
LSS X'15'
LSS X'17'
LSS X'19'
LSS X'1B'
Server0
Extent Pool CKD-1
Rank-a
Rank-b
Extent Pool FB-1
Rank-c
Rank-d
LSS X'1D'
Server1
Extent Pool CKD-2
Rank-w
Rank-x
Extent Pool FB-2
Rank-y
Rank-z
X'0E00'
X'0E01'
X'1800'
X'0500'
X'0D00'
X'1100'
Volume ID
X'1101'
LSS X'1F'