Appendix B. Using the DS6000 with iSeries 355
Number of iSeries Fibre Channel adapters
The most important factor to take into consideration when calculating the number of Fibre
Channel adapters in the iSeries is the throughput capacity of the adapter and IOP
combination.
Since this guideline is based only on iSeries adapters and Access Density (AD) of iSeries
workload, it doesn't change when using the DS6000. (The same guidelines are valid for ESS
800).
Table B-2 shows the approximate capacity which can be supported with various IOA/IOP
combinations.
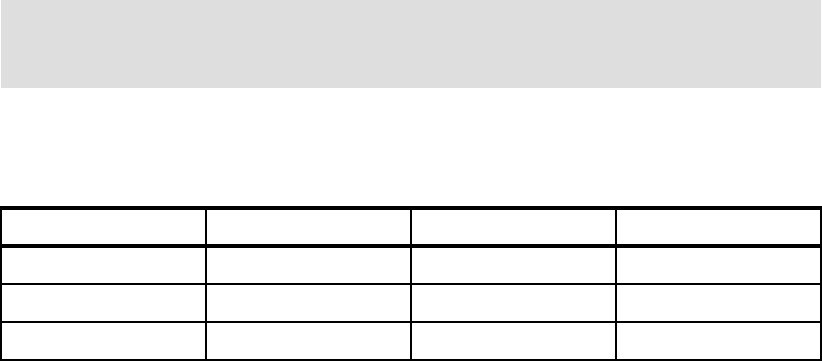
Table B-2 Capacity per I/O Adapter
For most iSeries workloads, Access Density is usually below 2, so if you do not know it, the
Rule of thumb column is a typical value to use.
Size and number of LUNs
As discussed in “Logical volume sizes” on page 330, OS/400 can only use fixed logical
volume sizes. As a general rule of thumb, we recommend that you should configure more
logical volumes than actual DDMs. As a minimum, we recommend 2:1. For example, with 73
GB DDMs, you should use a maximum size of 35.1GB LUNs. The reason for this is that
OS/400 does not support command tag queuing. Using more, smaller LUNs can reduce I/O
queues and wait times by allowing OS/400 to support more parallel I/Os.
From the values in Table B-2, you can calculate the number of iSeries Fibre Channel adapters
for your required iSeries disk capacity. As each I/O adapter can support a maximum of 32
LUNs, divide the capacity per adapter by 32 to give the approximate average size of each
LUN.
For example, assume you require 2TB capacity and are using 2787 I/O adapters with 2844
I/O processors. If you know the access density, calculate the capacity per I/O adapter, or use
the rule-of-thumb. Let’s assume the rule-of-thumb of 500GB per adapter. In this case, we
would require four I/O adapters to support the workload. If we were able to have variable
LUNs sizes, we could support 32 15.6GB LUNs per I/O adapter. However, since OS/400 only
supports fixed volume sizes, we could support 28 17.5GB volumes to give us approximately
492GB per adapter.
Recommended number of ranks
As a general guideline, you may consider 1500 disk operations/second for an average RAID
rank.
Note: Access Density is the capacity of occupied disk space divided by the average I/O
per sec. These values can be obtained from the OS/400 System, Component and
Resource Interval performance reports.
I/O Adapter I/O Processor Capacity per IOA Rule of thumb
2787 2844 1022/AD 500GB
2766 2844 798/AD 400GB
2766 2843 644/AD 320GB