Chapter 3. RAS 51
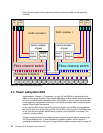
A logic or power failure in a SAN switch can interrupt communication between hosts and the
DS6800. We recommend that more than one SAN switch be provided to ensure continued
availability. For example, four of the eight fibre ports in a DS6800 could be configured to go
through each of two directors. The complete failure of either director leaves half of the paths
still operating.
Multipathing software
For each attached host we now require a mechanism to allow the attached operating system
to manage multiple paths to the same device, and to also show a preference in this routing so
that I/O requests for each LUN go to the preferred controller. Also, when a controller failover
occurs, attached hosts that were routing all I/O for a particular group of LUNs (LUNs on either
even or odd LSSs) to a particular controller (because it was the preferred controller) must
have a mechanism to allow them to detect that the preferred path is gone. It should then be
able to re-route all I/O for those LUNs to the alternate, previously non-preferred controller.
Finally, it should be able to detect when a controller comes back online so that I/O can now
be directed back to the preferred controller on a LUN by LUN basis (determined by which
LSS a LUN is a member of). The mechanism that will be used varies by the attached host
operating system, as detailed in the next two sections.
3.2.1 Open systems host connection
In the majority of open systems environments, IBM recommends the use of the Subsystem
Device Driver (SDD) to manage both path failover and preferred path determination. SDD is
supplied free of charge to all IBM customers who use ESS 2105, SAN Volume Controller
(SVC), DS6800, or DS8000. A new version of SDD (Version 1.6) will also allow SDD to
manage pathing to the DS6800 and DS8000.
SDD provides availability through automatic I/O path failover. If a failure occurs in the data
path between the host and the DS6800, SDD automatically switches the I/O to another path.
SDD will also set the failed path back online after a repair is made. SDD also improves
performance by sharing I/O operations to a common disk over multiple active paths to
distribute and balance the I/O workload. SDD also supports the concept of preferred path.
SDD is not available for all supported operating systems, so attention should be directed to
the IBM TotalStorage DS6000 Host Systems Attachment Guide, GC26-7680, and the
interoperability Web site for direction as to which multi-pathing software will be required.
Some devices, such as the IBM SAN Volume Controller (SVC), do not require any
multi-pathing software because the internal software in the device already supports multi-
pathing and preferred path. The interoperability Web site is located at:
http://www.ibm.com/servers/storage/disk/ds6000/interop.html
3.2.2 zSeries host connection
In the zSeries environment, the normal practice is to provide multiple paths from each host to
a disk subsystem. Typically, four paths are installed. The channels in each host that can
access each Logical Control Unit (LCU) in the DS6800 are defined in the HCD (or IOCDS) for
that host. Dynamic Path Selection (DPS) allows the channel subsystem to select any
available (non-busy) path to initiate an operation to the disk subsystem. Dynamic Path
Reconnect (DPR) allows the DS6800 to select any available path to a host to reconnect and
resume a disconnected operation, for example, to transfer data after disconnection due to a
cache miss.
These functions are part of the zSeries architecture and are managed by the channel
subsystem in the host and the DS6800.