296 DS6000 Series: Concepts and Architecture
Metro Mirror and Global Copy
From a local data migration point of view both methods are on par with each other, with
Global Copy having a smaller impact on the subsystem performance and Metro Mirror
requiring almost no time for the final synchronization phase. It is advisable to use Global Copy
instead of Metro Mirror, if the source system is already at its performance limit even without
remote mirroring. Figure 15-6 outlines the migration steps.
Figure 15-6 Migration with Metro Mirror or Global Copy
The remote copy functionality can be used to migrate data in either direction between the
Enterprise Storage Server (ESS) 750 or 800 and the new DS8000 and DS6000 storage
systems. The ESS E20 and F20 lack support for remote copy over Fibre Channel and can
therefore not be mirrored directly to a DS6000.
Combination of Metro Mirror and Global Copy
A cascading Metro Mirror and Global Copy solution is useful in two cases:
The source system is already mirrored for disaster tolerance and mirroring is mandatory
for production. Then a Global Copy relationship can be used to migrate the data from the
secondary volumes of the Metro Mirror pair to the new machine.
Data must be migrated from an older ESS E20 or F20. Here a Metro Mirror using ESCON
connectivity is used to mirror the data to an intermediate ESS 800, which in turn will copy
the data to the DS8000 with Global Copy.
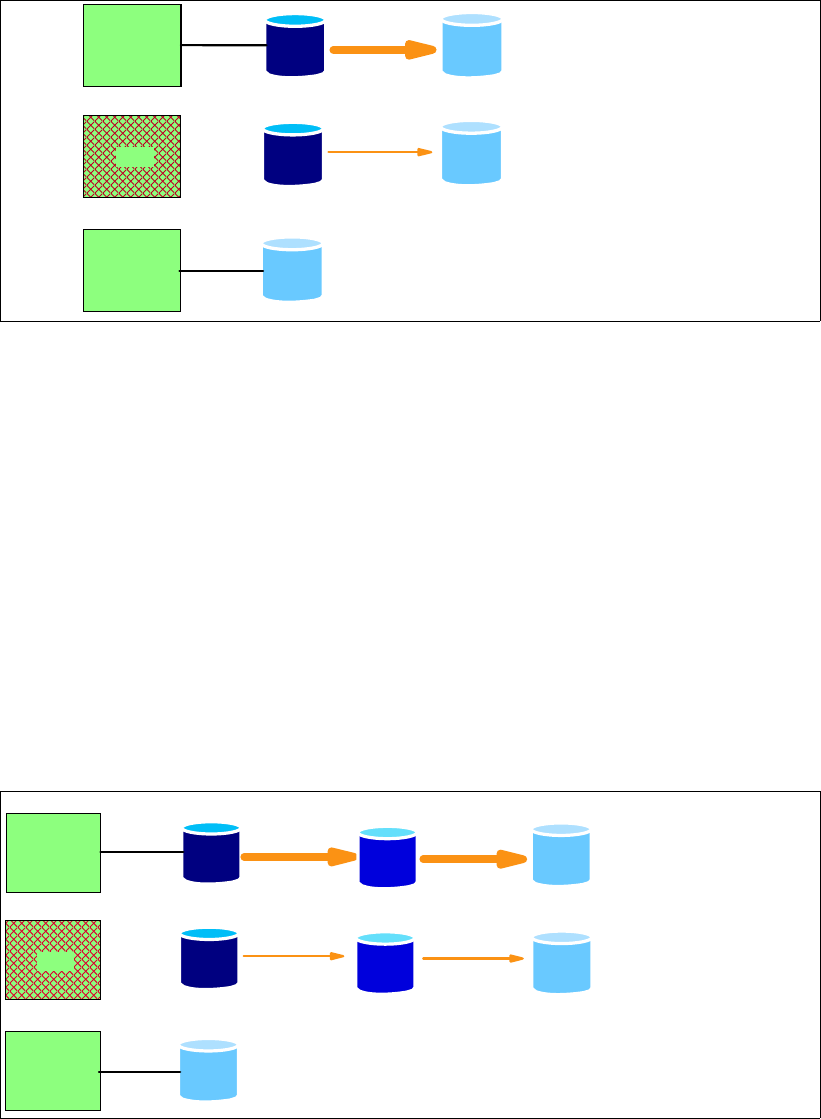
Figure 15-7 shows the setup and steps to take for this method.
Figure 15-7 Migration with Metro Mirror, Global Copy and an intermediate device
Initial Copy
Host
Continuous updates
Host
Final synchronization
Stop applications
Host
Restart
Using new copy
Host
Restart
Using new copy
Host
Final synchronization
Stop applications
Initial Copy
Host
Continuous updates
Intermediate Device
Metro Mirror
Global Copy


















