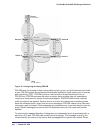
Subnet 192.168.1.0/24
Source
Port
Port 1/0/9
Port
Subnet 192.168.3.0/24
IP 192.168.1.1
1/0/13
1/0/1
Subnet 192.168.6.0/24
Subnet 192.168.2.0/24
Subnet 192.168.5.0/24
Subnet 192.168.4.0/24
Host
IP 192.168.4.2
Port 1/0/10
Port
1/0/11
Port
1/0/21
Port 1/0/22
Switch A
Switch D
Switch B
Switch C
Port 1/0/22
Port
1/0/24
Port
1/0/21
436 | Chapter 28. PIM
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Figure 45. Configuring and Using PIM-DM
PIM-DM uses the existing unicast routing table and join, prune, and graft mechanism to build
a tree. PIM-DM creates source-based shortest-path distribution trees making use of reverse
path forwarding (RPF). PIM-DM cannot be used to build a shared distribution tree, as
PIM-SM can. PIM-DM assumes that when a sender starts sending data, all downstream
routers and hosts want to receive a multicast datagram. PIM-DM initially floods multicast
traffic throughout the network. Routers that do not have any downstream neighbors prune
back the unwanted traffic. Apart from the prune messages, PIM-DM makes use of two more
messages: graft and assert. Graft messages are used whenever a new host wants to join the
group. Assert messages are used to shut off duplicate flows onto the same multi-access
network.
To minimize the repeated flooding of datagrams and subsequent pruning associated with a
particular (S,G) pair
, PIM-DM uses a state refresh message. This message is sent by the
routers directly connected to the source and is propagated throughout the network. When