User's Guide
Code Sets D-47
Table D-6. Epson and IBM Escape Sequences––continued
Function ASCII Hexadecimal Decimal Description
Graphic Functions––continued
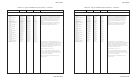
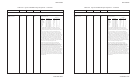
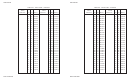
Print IBM XL24 ....................... ESC [ g n1 n2 1B 5B 67 n1 n2 27 91 103 n1 n2 Variable m in the sequences determines which graphics
graphics (continued) m list m list m list mode the printer uses:
Variable m
Mode Resolution ASCII Hex Dec
Single 72V x 60H dpi NUL 00 0
Double 72V x 120H dpi SOH 01 1
HS double 72V x 120H dpi STX 02 2
Quadruple 72V x 240H dpi ETX 03 3
Single 180V x 60H dpi BS 08 8
Double 180V x 120H dpi HT 09 9
Triple 180V x 180H dpi VT 0B 11
Hex 180V x 360H dpi FF 0C 12
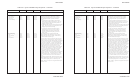
In the HS double, quadruple and hex modes, consecutive
horizontal dots are not permitted. If the sequence specifies
consecutive horizontal dots, the printer does not print the second
dot.
The list in the sequence is a series of codes that define the
columns to print. Modes with 72 dots per vertical inch print 8-
dot-high columns. For these modes, the first code defines the
first column, the second code defines the sec-ond column, and so
on. Each bit in a code controls a specific dot in the column. The
most significant bit controls the top dot, the next bit controls the
second dot, and so on. If the bit is "1", the dot prints; if the bit is
"0", the dot does not print. For example, FF hex prints all eight
dots in the col-umn, 00 hex prints no dots, 0F hex prints the lower
four dots, and F0 hex prints the upper four dots.
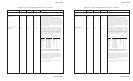
Modes with 180 dots per vertical inch print 24-dot-high-
columns. The first three codes define the first column, the
second three codes define the second column, and so on. Each
bit in a code controls a specific dot in the column. The most
significant bit of the first code controls the top dot, the next bit
controls the second dot, and so on. The most significant bit of the
second code controls the ninth dot from the top, the next bit
controls the tenth dot, and so on. And finally, the most significant
bit of the third code controls the 17th dot from the top, the next bit
controls the 18th dot, and so on. If the bit is "1", the dot prints; if
the bit is "0", the dot does not print. For example, FF FF FF hex
prints all 24 dots in the column, 00 00 00 hex prints no dots, 00 FF
00 hex prints the middle eight dots, and 80 00 01 hex prints the top
and bottom dots.
User's Guide
Code Sets D-47
Table D-6. Epson and IBM Escape Sequences––continued
Function ASCII Hexadecimal Decimal Description
Graphic Functions––continued
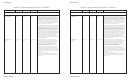
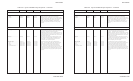
Print IBM XL24 ....................... ESC [ g n1 n2 1B 5B 67 n1 n2 27 91 103 n1 n2 Variable m in the sequences determines which graphics
graphics (continued) m list m list m list mode the printer uses:
Variable m
Mode Resolution ASCII Hex Dec
Single 72V x 60H dpi NUL 00 0
Double 72V x 120H dpi SOH 01 1
HS double 72V x 120H dpi STX 02 2
Quadruple 72V x 240H dpi ETX 03 3
Single 180V x 60H dpi BS 08 8
Double 180V x 120H dpi HT 09 9
Triple 180V x 180H dpi VT 0B 11
Hex 180V x 360H dpi FF 0C 12
In the HS double, quadruple and hex modes, consecutive
horizontal dots are not permitted. If the sequence specifies
consecutive horizontal dots, the printer does not print the second
dot.
The list in the sequence is a series of codes that define the
columns to print. Modes with 72 dots per vertical inch print 8-
dot-high columns. For these modes, the first code defines the
first column, the second code defines the sec-ond column, and so
on. Each bit in a code controls a specific dot in the column. The
most significant bit controls the top dot, the next bit controls the
second dot, and so on. If the bit is "1", the dot prints; if the bit is
"0", the dot does not print. For example, FF hex prints all eight
dots in the col-umn, 00 hex prints no dots, 0F hex prints the lower
four dots, and F0 hex prints the upper four dots.
Modes with 180 dots per vertical inch print 24-dot-high-
columns. The first three codes define the first column, the
second three codes define the second column, and so on. Each
bit in a code controls a specific dot in the column. The most
significant bit of the first code controls the top dot, the next bit
controls the second dot, and so on. The most significant bit of the
second code controls the ninth dot from the top, the next bit
controls the tenth dot, and so on. And finally, the most significant
bit of the third code controls the 17th dot from the top, the next bit
controls the 18th dot, and so on. If the bit is "1", the dot prints; if
the bit is "0", the dot does not print. For example, FF FF FF hex
prints all 24 dots in the column, 00 00 00 hex prints no dots, 00 FF
00 hex prints the middle eight dots, and 80 00 01 hex prints the top
and bottom dots.