NPIV Proxy Gateway Operations and Capabilities
Benefits of an NPIV Proxy Gateway
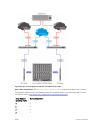
The MXL 10/40GbE Switch and M I/O Aggregator with the FC Flex IO module functions as a top-of-rack
edge switch that supports Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE) traffic — FCoE for storage, Interprocess
Communication (IPC) for servers, and Ethernet LAN (IP cloud) for data — as well as Fibre Channel (FC)
links to one or more SAN fabrics.
Using an NPIV proxy gateway (NPG) helps resolve the following problems in a storage area network:
• Fibre Channel storage networks typically consist of servers connected to edge switches, which are
connected to SAN core switches. As the SAN grows, it is necessary to add more ports and SAN
switches. This results in an increase in the required domain IDs, which may surpass the upper limit of
239 domain IDs supported in the SAN network. An NPG avoids the need for additional domain IDs
because it is deployed outside the SAN and uses the domain IDs of core switches in its FCoE links.
• With the introduction of 10GbE links, FCoE is being implemented for server connections to optimize
performance. However, a SAN traditionally uses Fibre Channel to transmit storage traffic. FCoE servers
require an efficient and scalable bridging feature to access FC storage arrays, which an NPG provides.
NPIV Proxy Gateway Operation
Consider a sample scenario of NPG operation. An M1000e chassis configured as an NPG does not join a
SAN fabric, but functions as an FCoE-FC bridge that forwards storage traffic between servers and core
SAN switches. The core switches forward SAN traffic to and from FC storage arrays.
An M1000e chassis FC port is configured as an N (node) port that logs in to an F (fabric) port on the
upstream FC core switch and creates a channel for N-port identifier virtualization. NPIV allows multiple
N-port fabric logins at the same time on a single, physical Fibre Channel link.
Converged Network Adapter (CNA) ports on servers connect to the M1000e chassis Ten-Gigabit Ethernet
ports and log in to an upstream FC core switch through the FC Flex IO module N port. Server fabric login
(FLOGI) requests are converted into fabric discovery (FDISC) requests before being forwarded by the FC
Flex IO module to the FC core switch.
Servers use CNA ports to connect over FCoE to an Ethernet port in ENode mode on the NPIV proxy
gateway. FCoE transit with FIP snooping is automatically enabled and configured on the M1000e gateway
to prevent unauthorized access and data transmission to the SAN network (see FCoE Transit). FIP is used
by server CNAs to discover an FCoE switch operating as an FCoE forwarder (FCF).
The NPIV proxy gateway aggregates multiple locally connected server CNA ports into one or more
upstream N port links, conserving the number of ports required on an upstream FC core switch while
providing an FCoE-to-FC bridging functionality. The upstream N ports on an M1000e can connect to the
same or multiple fabrics.
Using an FCoE map applied to downstream (server-facing) Ethernet ports and upstream (fabric-facing)
FC ports, you can configure the association between a SAN fabric and the FCoE VLAN that connects
1078
FC Flex IO Modules