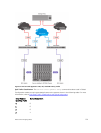
Example of Applying DCB PFC Input Policy and ETS Output Policy in a Switch Stack
dcb-map stack-unit all stack-ports all <dcb-map-name>
Applying DCB Policies in a Switch Stack
You can apply a DCB policy with PFC configuration to all stacked ports in a switch stack or on a stacked
switch. You can apply different DCB policies to different stacked switches.
To apply DCB policies in a switch stack, use the following command.
• Apply the specified DCB policy on all ports of the switch stack or a single stacked switch.
CONFIGURATION mode
dcb-map stack-unit all stack-ports all <dcb-map-name>
Configure a DCBx Operation
DCB devices use data center bridging exchange protocol (DCBx) to exchange configuration information
with directly connected peers using the link layer discovery protocol (LLDP) protocol.
DCBx can detect the misconfiguration of a peer DCB device, and optionally, configure peer DCB devices
with DCB feature settings to ensure consistent operation in a data center network.
DCBx is a prerequisite for using DCB features, such as priority-based flow control (PFC) and enhanced
traffic selection (ETS), to exchange link-level configurations in a converged Ethernet environment. DCBx
is also deployed in topologies that support lossless operation for FCoE or iSCSI traffic. In these scenarios,
all network devices are DCBx-enabled (DCBx is enabled end-to-end). For more information about how
these features are implemented and used, refer to:
• Configuring Priority-Based Flow Control
• Configure Enhanced Transmission Selection
• Configuring FIP Snooping
DCBx supports the following versions: CIN, CEE, and IEEE2.5.
Prerequisite: For DCBx, enable LLDP on all DCB devices.
DCBx Operation
DCBx performs the following operations:
• Discovers DCB configuration (such as PFC and ETS) in a peer device.
• Detects DCB mis-configuration in a peer device; that is, when DCB features are not compatibly
configured on a peer device and the local switch. Mis-configuration detection is feature-specific
because some DCB features support asymmetric configuration.
• Reconfigures a peer device with the DCB configuration from its configuration source if the peer
device is willing to accept configuration.
• Accepts the DCB configuration from a peer if a DCBx port is in “willing” mode to accept a peer’s DCB
settings and then internally propagates the received DCB configuration to its peer ports.
Data Center Bridging (DCB)
273