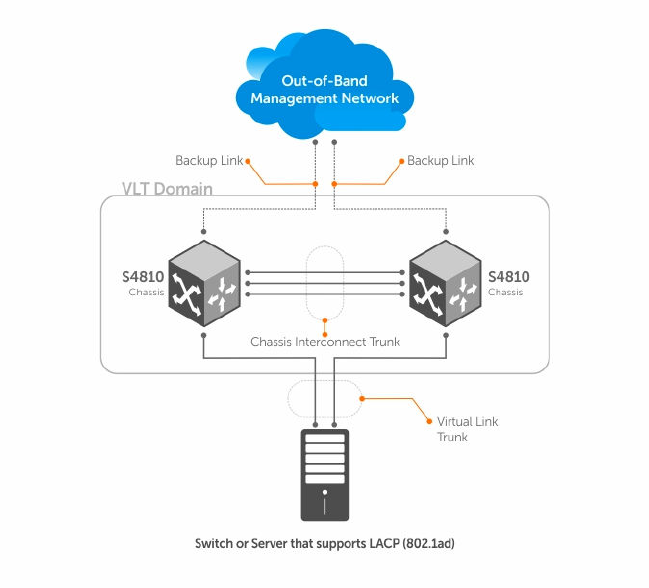
Figure 131. Virtual Link Trunking
Multi-domain VLT
A multi-domain VLT (mVLT) configuration creates a port channel between two VLT domains by allowing
two different VLT domains, using different VLT Domain ID numbers, connected by a standard LACP LAG
to form a loop-free Layer 2 topology in the aggregation layer.
This configuration supports a maximum of four (4) nodes per mVLT domain, increasing the number of
available ports and allowing for dual redundancy of the VLT.
Additionally, a VLT domain that is a member of one mVLT can be used in another mVLT configuration
with a different VLT domain. Routing protocols such as OSPF are not compatible with mVLT; however,
VLT domains can be used for routing. A separate Layer 3 router is not required for inter-VLAN
communication.
The following figure shows how the core/aggregation port density in the Layer 2 topology is increased
using mVLT. For inter-VLAN routing and other Layer 3 routing, a separate Layer 3 router is required.
960
Virtual Link Trunking (VLT)


















