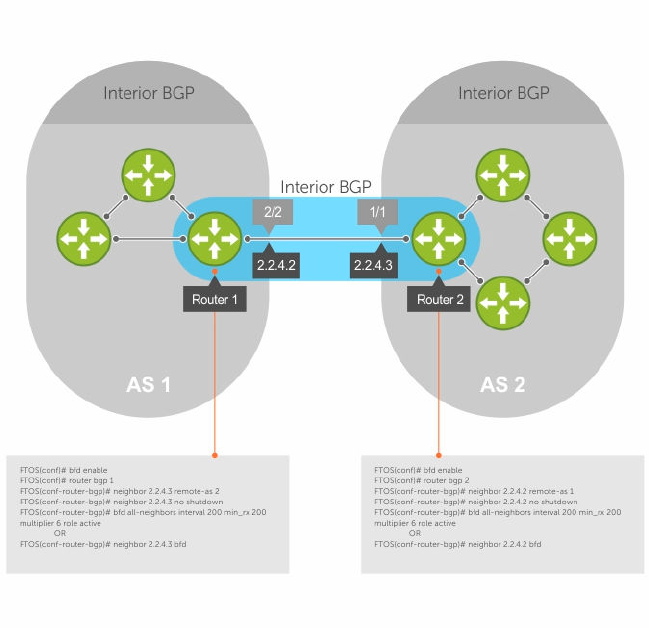
Figure 13. Establishing Sessions with BGP Neighbors
The sample configuration shows alternative ways to establish a BFD session with a BGP neighbor:
• By establishing BFD sessions with all neighbors discovered by BGP (the bfd all-neighbors
command).
• By establishing a BFD session with a specified BGP neighbor (the neighbor {ip-address | peer-
group-name
} bfd command)
BFD packets originating from a router are assigned to the highest priority egress queue to minimize
transmission delays. Incoming BFD control packets received from the BGP neighbor are assigned to the
highest priority queue within the control plane policing (CoPP) framework to avoid BFD packets drops
due to queue congestion.
BFD notifies BGP of any failure conditions that it detects on the link. Recovery actions are initiated by
BGP.
BFD for BGP is supported only on directly-connected BGP neighbors and only in BGP IPv4 networks.
As long as each BFD for BGP neighbor receives a BFD control packet within the configured BFD interval
for failure detection, the BFD session remains up and BGP maintains its adjacencies. If a BFD for BGP
neighbor does not receive a control packet within the detection interval, the router informs any clients of
the BFD session (other routing protocols) about the failure. It then depends on the individual routing
protocols that uses the BGP link to determine the appropriate response to the failure condition. The
typical response is to terminate the peering session for the routing protocol and reconverge by bypassing
the failed neighboring router. A log message is generated whenever BFD detects a failure condition.
160
Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD)


















