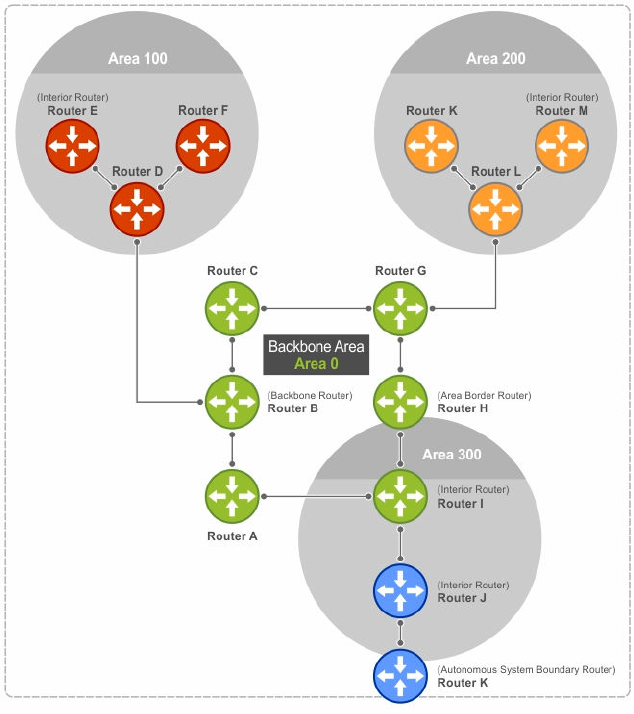
You can divide an AS into a number of areas, which are groups of contiguous networks and attached
hosts. Routers with multiple interfaces can participate in multiple areas. These routers, called area border
routers (ABRs), maintain separate databases for each area. Areas are a logical grouping of OSPF routers
identified by an integer or dotted-decimal number.
Areas allow you to further organize your routers within in the AS. One or more areas are required within
the AS. Areas are valuable in that they allow sub-networks to "hide" within the AS, thus minimizing the
size of the routing tables on all routers. An area within the AS may not see the details of another area’s
topology. AS areas are known by their area number or the router’s IP address.
Figure 94. Autonomous System Areas
Area Types
The backbone of the network is Area 0. It is also called Area 0.0.0.0 and is the core of any AS.
All other areas must connect to Area 0. Areas can be defined in such a way that the backbone is not
contiguous. In this case, backbone connectivity must be restored through virtual links. Virtual links are
configured between any backbone routers that share a link to a non-backbone area and function as if
they were direct links.
614
Open Shortest Path First (OSPFv2 and OSPFv3)


















