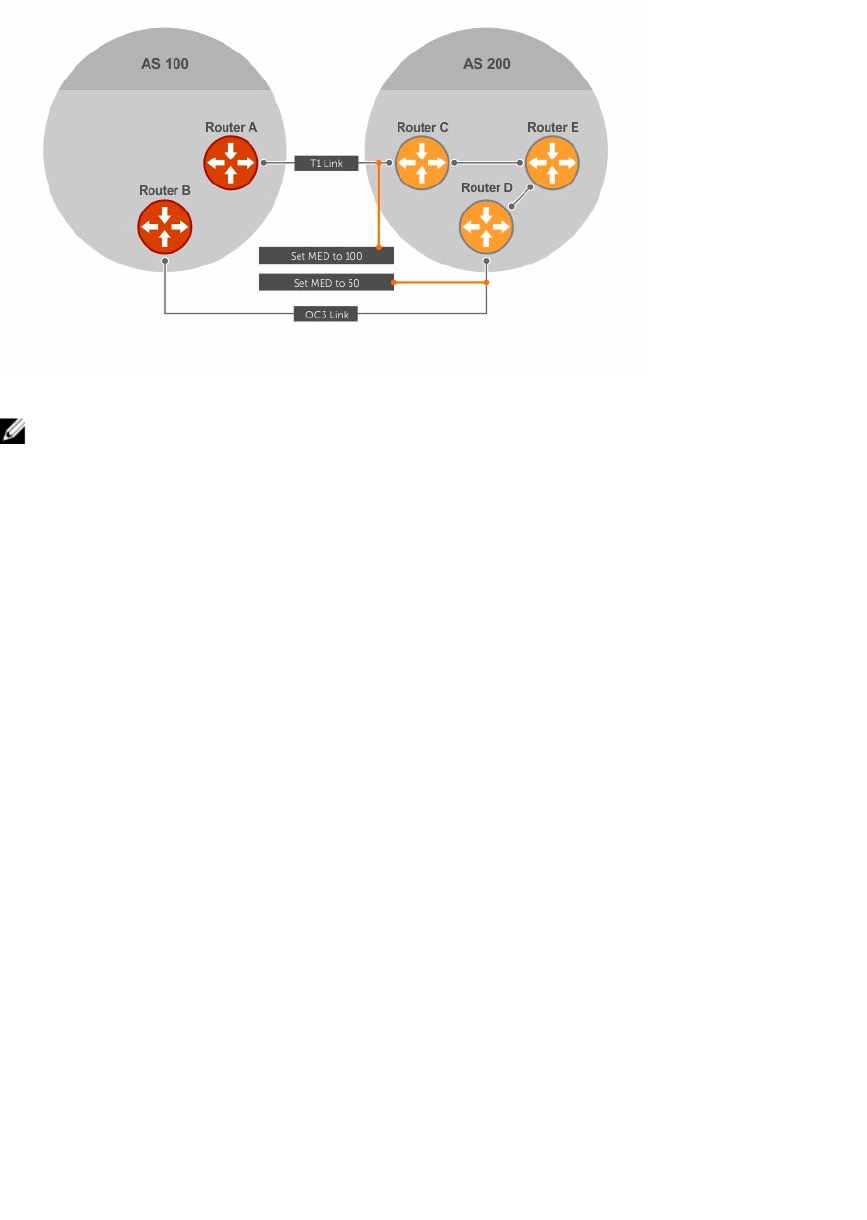
Figure 22. Multi-Exit Discriminators
NOTE: With the Dell Networking OS version 8.3.1.0, configuring the set metric-type internal
command in a route-map advertises the IGP cost as MED to outbound EBGP peers when
redistributing routes. The configured set metric value overwrites the default IGP cost.
Origin
The origin indicates the origin of the prefix, or how the prefix came into BGP. There are three origin
codes: IGP, EGP, INCOMPLETE.
Origin Type Description
IGP Indicates the prefix originated from information learned through an interior
gateway protocol.
EGP Indicates the prefix originated from information learned from an EGP protocol,
which NGP replaced.
INCOMPLETE Indicates that the prefix originated from an unknown source.
Generally, an IGP indicator means that the route was derived inside the originating AS. EGP generally
means that a route was learned from an external gateway protocol. An INCOMPLETE origin code
generally results from aggregation, redistribution, or other indirect ways of installing routes into BGP.
In the Dell Networking OS, these origin codes appear as shown in the following example. The question
mark (?) indicates an origin code of INCOMPLETE (shown in bold). The lower case letter (i) indicates an
origin code of IGP (shown in bold).
Example of Viewing Origin Codes
Dell#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 0, local router ID is 10.101.15.13
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best
Path source: I - internal, a - aggregate, c - confed-external, r -
redistributed, n - network
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
184
Border Gateway Protocol IPv4 (BGPv4)


















