26 www.emersonct.com SM-EZMotion Module User Guide
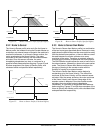
position. After completing an Absolute Index, the motor will
always be in the same position regardless of the starting
position of the motor. The direction that the motor moves
during an Absolute Index is dependant upon its position
when the index is initiated.
If an Absolute Index is initiated a second time, just after
completing the first index the motor will not move because
it is already at its specified absolute position.
Figures 41 and 42 show examples of an Absolute Index
profile.
Figure 41: Absolute Index Profile (Example 1)
Figure 42: Absolute Index Profile (Example 2)
Note
If Rotary Rollover is active, an Absolute Index will
take the shortest path to the specified index position.
5.4.2 Incremental Index
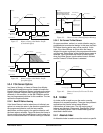
An Incremental Index is used to make the motor travel a
specified distance each time the index is initiated. The final
position after the Index is completed is entirely dependant
on the starting position before the Index was initiated.
If an Incremental Index is initiated a second time, it will
move the same distance each time.
Figures 43 and 44 show examples of an Incremental Index
profile.
Figure 43: Incremental Index Profile
Figure 44: Incremental Index - Repeated 3 Times
5.4.3 Registration Index
A Registration Index functions much the same as a Home
profile. The index runs at a specified velocity until a
registration signal activates. Once the signal activates, the
index either beings to decelerate immediately, or it
continues at velocity for a specified offset distance.
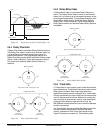
5.4.3.1 Registration to Sensor
In a Registration Index with Sensor defined as the
registration signal, the index travels at velocity until an
external sensor or switch activates. The sensor or switch
must be wired to a digital input on the SM-EZMotion
module, SP drive, or SM-IO Plus module. To get the
highest accuracy for the Registration to Sensor, an
SM-EZMotion module digital input must be used to take
advantage of the high-speed capture capability. Three
Figures below show examples of a Registration Index to
Sensor using different Offset values.
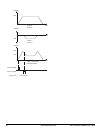
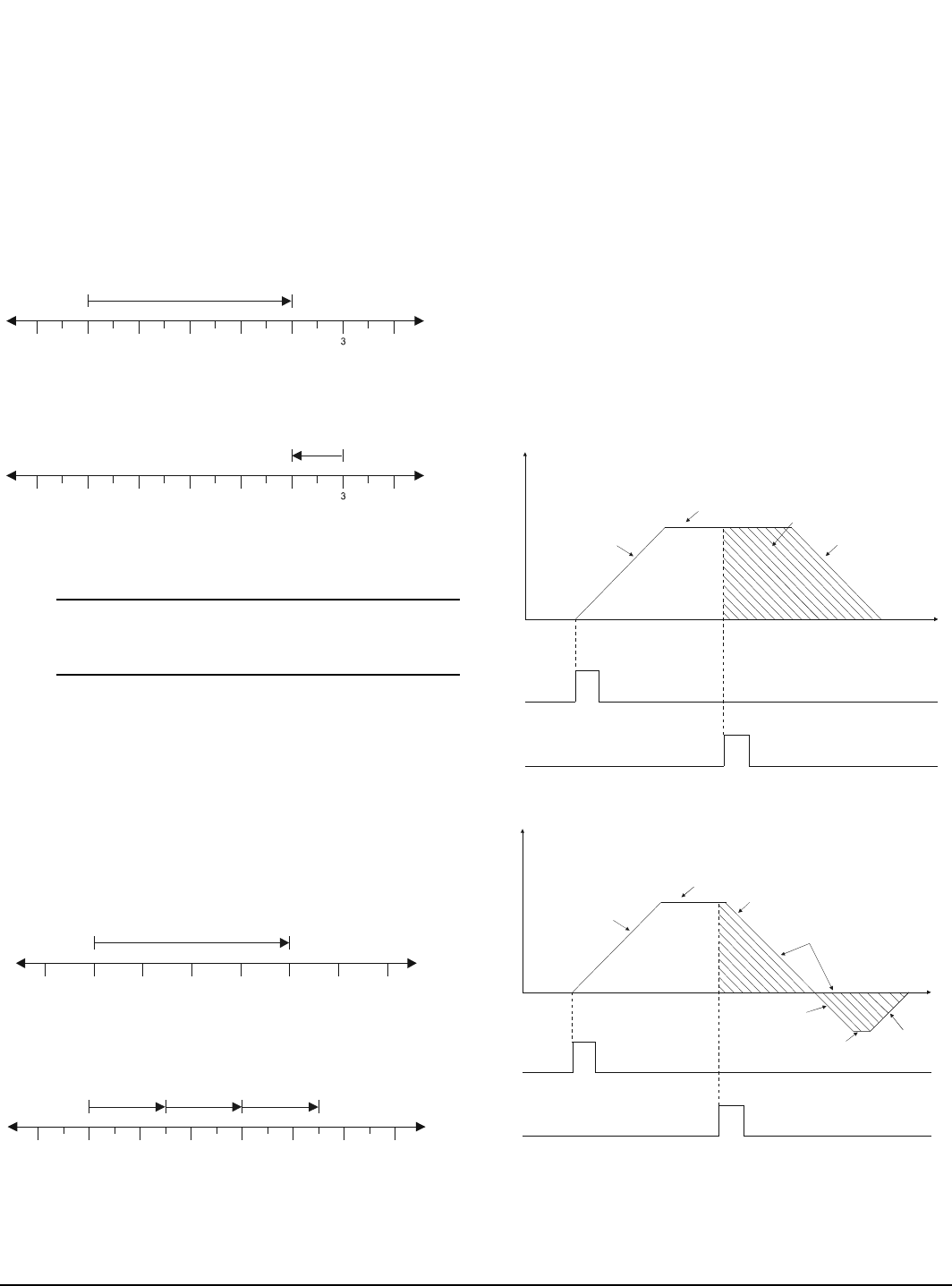
Figure 45: Registration to Sensor Profile (Offset > 0)
Figure 46: Registration to Sensor Profile (Offset = 0)
-2-4 -1 0 421
Starting Position: -2 Revs
In
de
x P
os
i
t
i
o
n: 2 R
e
v
s
Positio
n
(Revs)
-2-4 -1 0 421
Starting Position: 3 Revs
In
de
x P
os
i
t
i
o
n: 2 R
e
v
s
Positio
n
(Revs)
2134 8765
Starting Position: 2 Revs
Index Distance: 4 Revs
Positio
n
(Revs)
2146 1412108
Starting Position: 2 Revs
In
de
x Di
sta
n
ce
:
3
R
e
v
s
Positio
n
(Revs)
Velocity
Index Accel
Index Velocity
Index Decel
Time
Index Initiate
Registration Sensor
Index Registration Offset
Velocity
Index Accel
Index Velocity
Index Decel
Time
Index Initiate
Registration Sensor
Two areas are equal so motor
ends at exact registration positio
n
Index Accel
Index Velocity
Index
Decel