This soft copy for use by IBM employees only.
This code is also on the control point and is executed once the boot code
has finished. There are two copies of the code stored in the flash memory.
One of these copies is identified as current and is loaded into RAM during
the initialization process. This code is executed from RAM. The second
copy of the operational code allows new operational code to be loaded into
the control point while the control point is running, and then swapped (which
resets the ATM subsystem) when it is less disruptive to network operations.
•
FPGA Code
This code configures the various internal chips on the IBM 8285 base unit so
that they perform their desired ATM functions. There are two copies of the
FPGA code stored in flash memory. One of these copies is identified as
current code. The current code is loaded into the internal chips of the
appropriate components during the initialization process. The second copy
of the FPGA code allows new FPGA code to be loaded while the IBM 8285 is
operational, and then swapped (which resets the ATM subsystem) when it is
less disruptive to network operations.
The following sections describe the code levels that are currently shipped, are
announced, or are available in the future.
3.3.1 Control Point Levels
Table 1 lists the levels of control point code that are currently available for the
8285 switch.
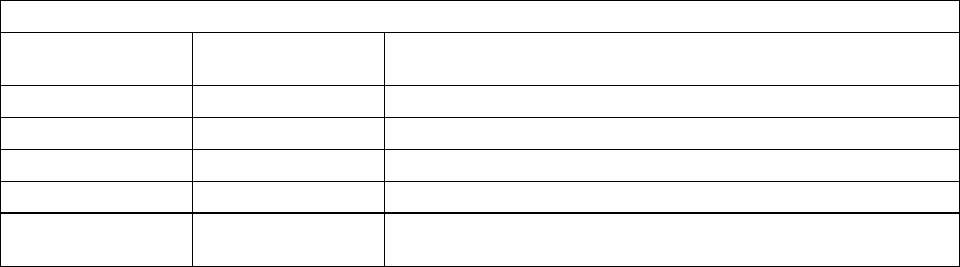
Table 1. Control Point Levels Summary of the IBM 8285 Nways ATM Workgroup Switch
Control Point
Level
Available Highlights
V1.0.0 March 1996 Initial release
V1.0.1 April 1996 Fixed some problems in initial release
V1.2.0 July 1996 TR LEC, EU, and 8260 modules support 1
V1.3.0 October 1996 New 8260 module support 2
V1.4.0 October 1996 Connection capacity increased, Variable VPC/VCI, ABR flow
control and PVC multipoint support3
Notes:
1 Except A-CPSW, MSS Server and 8271/8272 modules
2 A3-MB155 module
3 ATM firmware upgrade kit required
These control point microcode levels (except the obsolete ones) are available on
the Internet and can be downloaded via the Web or by FTP. And the code can
be downloaded into the IBM 8285 either out-of-band via a SLIP-connected
workstation, or inband via an FTP file transfer. For more information about how
to get and download the code, refer to 6.4, “Microcode/Picocode Considerations”
on page 110.
Chapter 3. Functional Overview of the IBM 8285 29


















