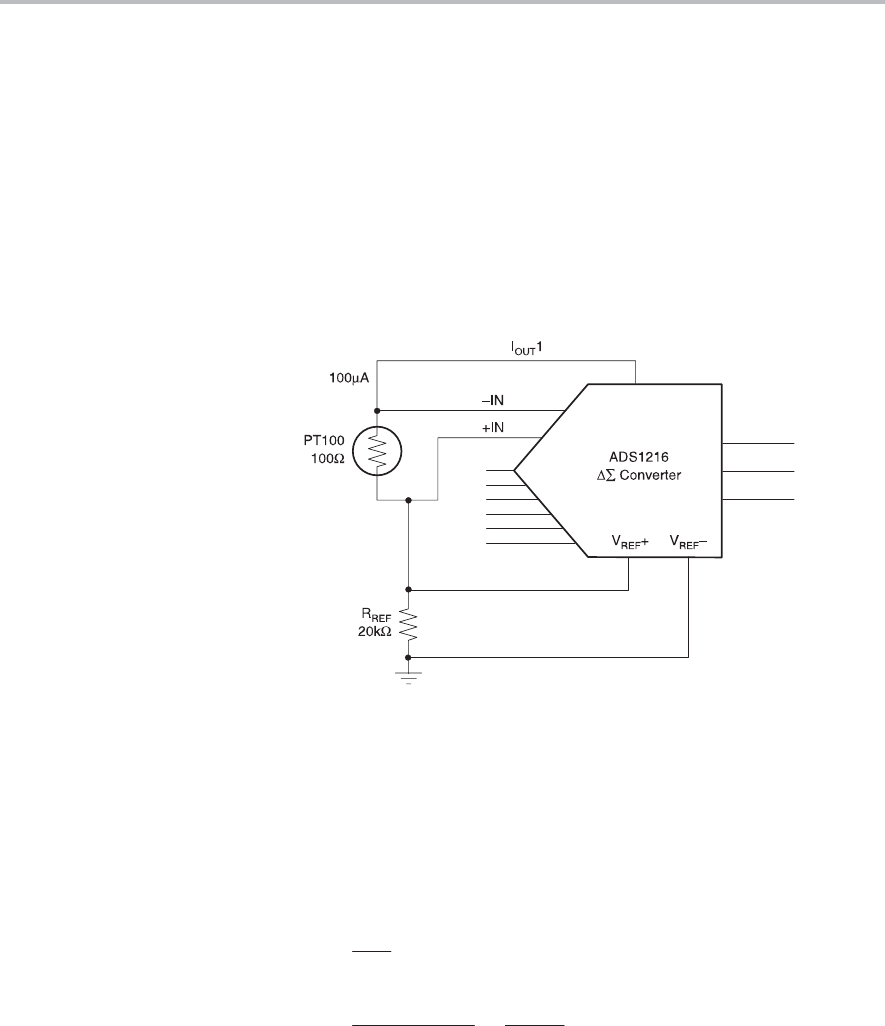
Ratiometric Measurements
12-24
12.16 Ratiometric Measurements
Ratiometric measurements may be used to eliminate potential inaccuracy
from the ADC process. Ratiometric measurements are obtained in a circuit
similar to the one shown in Figure 12−6, where the same source used to drive
the reference voltage (V
REF
) is used to drive the ADC (−IN). This allows
measurements to be taken without the accuracy of the voltage of V
REF
being
a factor in the measurement or in potential errors because the ratio between
the –IN and –V
REF
will be constant, regardless of the accuracy of the voltage
of +IN.
Figure 12−6. Circuit Drawing
The voltage measured is a ratio of the resistances R
REF
and PT100 because the
same current flows through the sense element (PT100) and the reference resistor
(R
REF
). Any errors in I
OUT
1 do not enter into the accuracy of the measurment be-
cause, as shown in the following equations, I
OUT
is effectively cancelled out:
V
IN
+ PT100 @ I
OUT
V
REF
+ R
REF
@ I
OUT
ADC Result +
V
IN
V
REF
ADC Result +
ǒ
PT100 @ I
OUT
Ǔ
ǒ
R
REF
@ I
OUT
Ǔ
+
PT100
R
REF
This eliminates both the reference voltage and the current source as sources
of accuracy error and is only limited by the accuracy of the reference resistor
and performance of the PT100. A high-precision reference resistor is readily
obtainable. This is much easier than trying to get the same precision and accu-
racy from a voltage reference.


















