8052 Instruction Set
E-3
8052 Instruction Set
E.2 8052 Instruction Set
ACALL Absolute Call within 2k Block
Syntax ACALL codeAddress
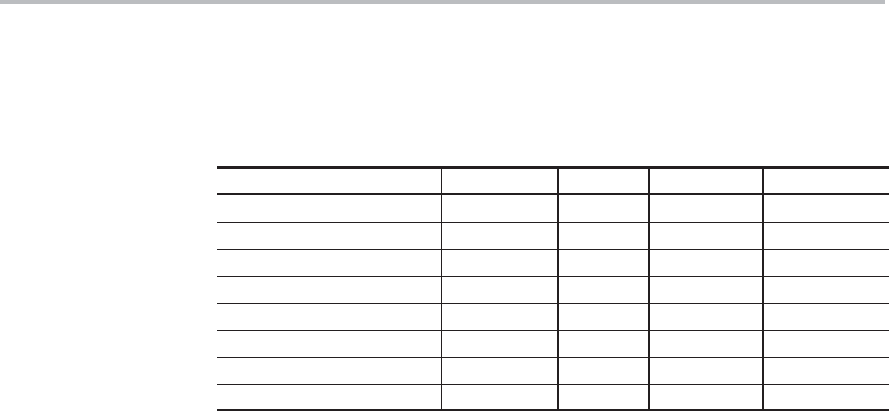
Instructions OpCode Bytes Cycles Flags
ACALL pg0Addr 0x11 2 2 None
ACALL pg1Addr 0x31 2 2 None
ACALL pg2Addr 0x51 2 2 None
ACALL pg3Addr 0x71 2 2 None
ACALL pg4Addr 0x91 2 2 None
ACALL pg5Addr 0xB1 2 2 None
ACALL pg6Addr 0xD1 2 2 None
ACALL pg7Addr 0xF1 2 2 None
ACALL unconditionally calls a subroutine at the indicated code address.
ACALL pushes the address of the instruction that follows ACALL onto the
stack, least significant byte first, and most significant byte second. The
program counter is then updated so that program execution continues at the
indicated address.
The new value for the program counter is calculated by replacing the
least-significant-byte of the program counter with the second byte of the
ACALL instruction, and replacing bits 0−2 of the most-significant-byte of the
program counter with bits 5−7 of the opcode value. Bits 3−7 of the
most-significant-byte of the program counter remain unchaged.
Calls must only be made to routines located within the same 2k block as the
first byte that follows ACALL because only 11 bits of the program counter are
affected by ACALL.
See also: LCALL, RET


















