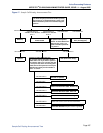
Voice Processing Features
INTER-TEL
®
CS-5200/5400 ADMINISTRATOR GUIDE, ISSUE 1.1 – August 2005
Page 274 E-mail Reader
When the caller accepts the directory name from voice mail, the caller is transferred to the cor-
responding mailbox. After the transfer the caller either hears the subscriber’s recorded greet-
ing, their recorded directory name, or, if no recording has been made, the “mailbox number
XXX is not available” prompt. The caller can then record a message.
When the caller accepts the directory name from the Automated Attendant, the caller is trans-
ferred to the selected destination (endpoint or mailbox) if it is available. If the destination is not
available, the caller is transferred to the associated mailbox, if one exists.
E-mail Reader
The EM voice processing system supports E-mail Reader which, if enabled, provides access to
voice mail, e-mail, and fax messages that are located in an advanced mailbox. E-mail Reader
uses Text-to-Speech (TTS) capabilities to convert the text in an e-mail message to a .wav file.
When the user accesses an e-mail message, E-Mail Reader announces the e-mail according to
the envelope options that the user set. Then, after the envelope is played, E-mail Reader reads
the text in the body of the message. Additional options for e-mail messages include reply, for-
ward, save, and delete. E-mail Reader is supported only on EM voice processing systems.
When the user accesses a fax message, E-mail Reader announces the fax envelope according to
the envelope options that the user set up. Because a fax message is received by the e-mail
server as an attachment to an e-mail message in the form of a .tif file, E-mail Reader cannot
read the text in the body of the fax. To view a fax and read it, users must access it from their e-
mail account. Fax options include saving, deleting, and forwarding to another fax machine.
For detailed information about using standard voice mailboxes and advanced mailboxes with
E-mail Reader capabilities, see the appropriate endpoint user guide.
Fax-On-Demand
The Fax-On-Demand feature provides fax services to callers. It is a specially programmed Call
Routing Announcement application that uses digit translation to allow callers to select the doc-
uments they want to have faxed to them.
With Fax-On-Demand, callers can use a DTMF endpoint to request one or more documents
from the company’s fax library, the library that is also used in the Unified Messaging faxing
feature. When the request is completed, the voice processing system places a call to the caller’s
fax machine to deliver the requested documents.
The Fax-On-Demand process is shown in the following steps:
1. The caller reaches the Call Routing Announcement application either through direct
ring-in or transfer.
2. After listening to the introductory recording, the caller selects a document by entering a
document number or using digit translation, depending on digit translation node pro-
gramming. If the document is selected by number, the system will ask the caller to ver-
ify the entry by pressing #. If the number is invalid, the system alerts the caller and
returns to the introductory recording.
3. The system checks the availability of the document, and one of the following occurs:
• If the document is available, the system tells the caller how many documents have
been selected and how many more documents can be requested (as determined by
the Maximum Selections Allowed value in the database). It then returns to the
recording to allow the caller to select more documents or end the selection process.
• If the document has been deleted or is being updated, the caller is told that the doc-
ument is unavailable and returns to the recording.