AI2524 Router Card User’s Manual
Page 9-2 August 1997
2524UM
Understand
Addresses
Addresses in the ISO network architecture are referred to as NSAP ad-
dresses and network entity titles (NETs). Each node in an OSI network
has one or more NETs. In addition, each node has many NSAP ad-
dresses. Each NSAP address differs from one of the NETs for that
node in only the last byte. This byte is called the N-selector. Its func-
tion is similar to the port number in other protocol suites.
The AI2524 router supports all NSAP address formats that are defined
by ISO 8348/Ad2; however, the AI2524 router provides ISO IGRP o
IS-IS dynamic routing only for NSAP addresses that conform to the
address constraints defined in the ISO standard for IS-IS (ISO 10589).
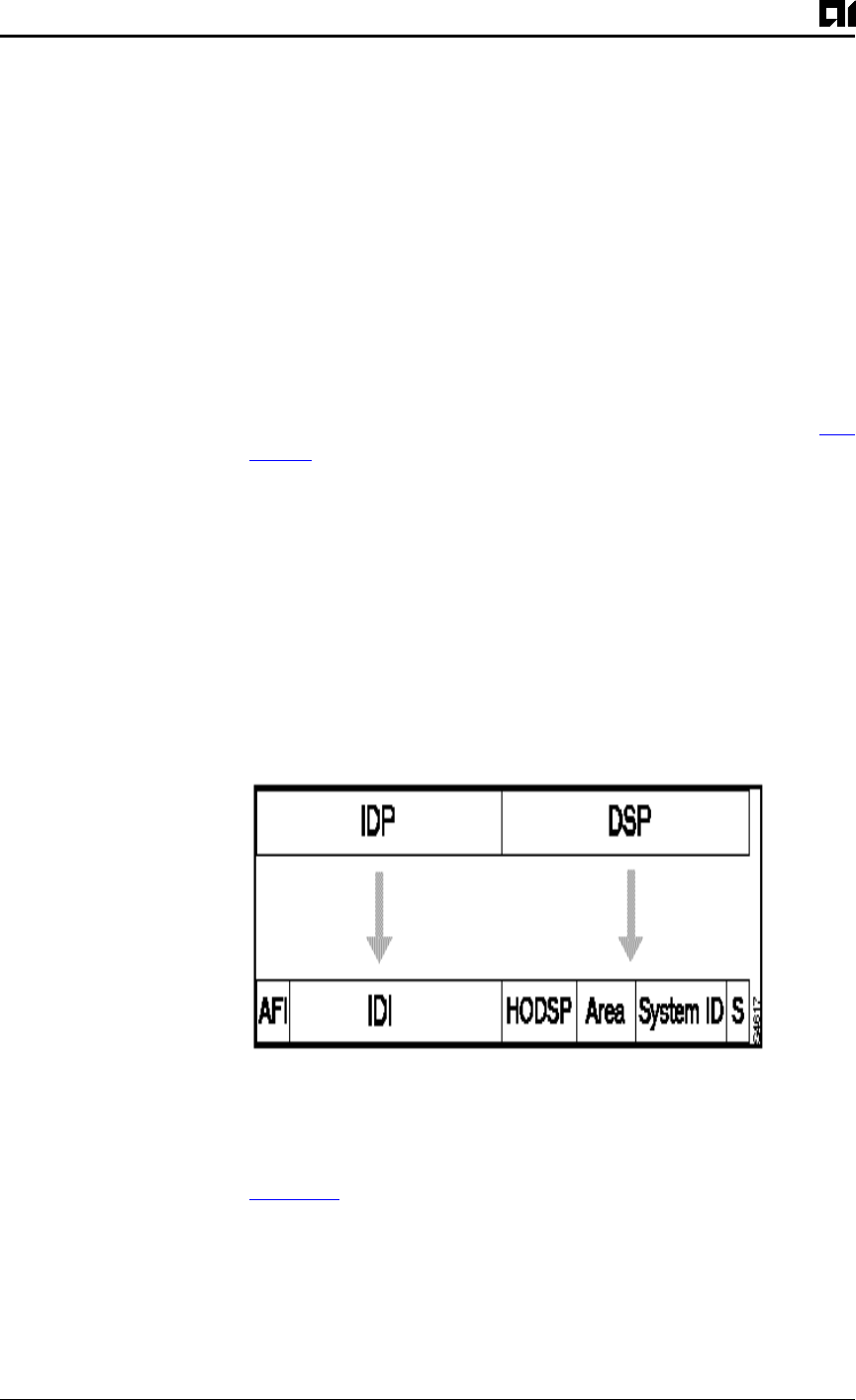
An NSAP address consists of these two major fields, as shown in Fig-
ure 9-1:
z
The initial domain p art (IDP) is made up of 1-byte authority and
format identifier (AFI) and a variable-length initial
domai nidentifier (IDI). The length of the IDI and the encoding
format for the domai nspecific part (DSP) are based on the value
of the AFI.
z
The DSP is made up of a high-order DSP, an area identifier, a sys-
tem identifier, and a 1-byte N-selector (labeled S).
Figure 9-1:NSAP Address Fields
Assign addresses or NETs for your domains and areas. Th
domai naddress uniquely identifies the routing domain. All routers
within a given doma inare given the same dom ainaddress. Within
each routing domain, you can set up one or more areas, as shown in
Figure 9-2. Determine which routers are to be assigned to which areas.


















