Chapter 9: AI2524 OSI/CLNP Configuration Steps
August 1997 Page 9-5
2524UM
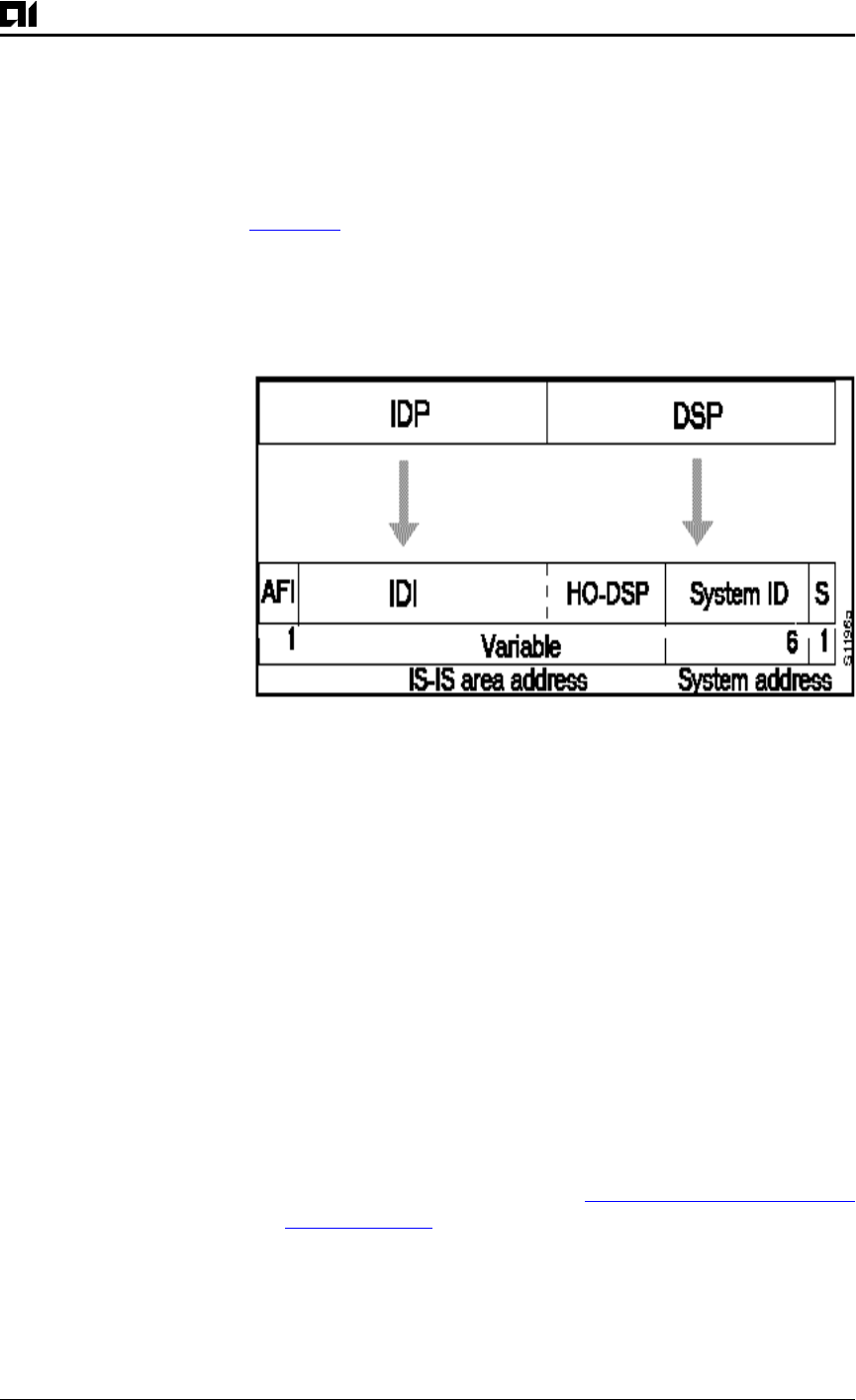
The IS-IS routing protocol interprets the bytes from the AFI up to (but
not including) the system ID field in the DSP as an area identifier. Th
system ID specifies the system.
Figure 9-4
illustrates the IS-IS NSAP addressing structure. The maxi-
mum address size is 20 bytes.
Figure 9-4:IS-IS NSAP Addressing Structure
Addressing Rules
All NSAP addresses must obey these constraints:
z
No two nodes can have addresses with the same NET; that is, ad-
dresses that match all but the N-selector (S) field in the DSP.
z
No two nodes residing within the same area can have addresses in
which the system ID fields are the same.
z
ISO IGRP requires at least 10 bytes of length: 1 byte for domain,
2 bytes for area, 6 bytes for system ID, and 1 byte for N-selector.
z
ISO IGRP and IS-IS should not be configured for the same area.
Do not specify an NSAP address where all bytes up to (but not in-
cluding) the system ID are the same when enabling both ISO
IGRP and IS-IS routing.
z
A router can have one or more area addresses. The concept of mul-
tiple area addresses is described in Assign Multiple Area Address-
es to IS-IS Areas.
z
IS-IS requires at least 8 bytes: one byte for area, 6 bytes for system
ID, and 1 byte for N-selector.


















