Chapter 8: Virtual LANs and GVRP
104 Section I: Using the Menus Interface
VLAN Features
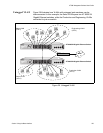
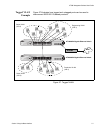
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a logical grouping of devices on
different physical LAN segments that allows users to communicate as if
they were physically connected to a single LAN, independent of the
physical configuration of the network.
With VLANs, you can segment your network and group end-nodes with
related functions into their own separate, logical LAN segments. For
example, the marketing personnel in your company may be spread
throughout a building. Assigning marketing to a single VLAN allows
marketing personnel to share resources and bandwidth as if they were
connected to the same segment. The resources of other departments can
be visible to the marketing VLAN members, accessible, or accessible only
to specified individuals.
A few benefits of a VLAN architecture are described in the following
sections.
Increased
Performance
In traditional Layer 2 switched networks, broadcast packets are sent to
each and every individual port. Grouping users into logical networks limits
broadcast traffic to users performing similar functions or users within
individual workgroups. High traffic, the danger of broadcast storms, router
latency, and data collisions are significantly reduced, and the efficiency of
the entire network is improved.
Improved
Manageability
VLANs provide a fundamental improvement in the design, administration,
and management of LANs. Before VLANs, physical changes to a network
were made at the switch in the wiring closet.
For example, if an employee transferred to a new department, changing
that employee’s LAN segment assignment often required a physical wiring
change at the switch.
As a software-base solution, VLANs eliminate the restriction of existing
network design and cabling infrastructure and allow the centralized
configuration of switches located in many different locations. VLAN
memberships are changed quickly and efficiently from the management
console rather than in a wiring closet.
Increased
Security
VLANs provide additional security not available in a shared media network
environment. Because a switched network only delivers frames to
intended recipients, and only broadcast frames to other members of the
VLAN, a network administrator can segment users requiring access to
sensitive information into separate VLANs from the rest of the general
user community.