Three-wire Interface Operation
The 3-wire interface is an industry standard motor control interface. This function uses
two inputs for momentary contact start/stop control, and a third for selecting forward or
reverse direction. To implement the 3-wire interface, assign 20 [STA] (Start), 21 [STP]
(Stop), and 22 [F/R] (Forward/Reverse) to three of the intelligent input terminals. Use a
momentary contact for Start and Stop. Use a selector switch, such as SPST for the
Forward/Reverse input. Be sure to set the operation command selection A002=01 for
input terminal control of motor.
If you have a motor control interface that needs logic-level control (rather than
momentary pulse control), use the [FW] and [RV] inputs instead.
Option
Code
Terminal
Symbol
Function Name State Description
ON Start motor rotation on momentary contact (uses
acceleration profile)
20 STA Start Motor
OFF No change to motor operation
ON No change to motor operation21 STP Stop Motor
OFF Stop motor rotation on momentary contact (use
deceleration profile)
ON Select reverse direction of rotation22 F/R Forward/Reverse
OFF Select forward direction of rotation
Valid for inputs: C001~C005
Required settings A002 = 01
Notes:
• The STP logic is inverted. Normally the switch
will be closed, so you open the switch to stop. In
this way, a broken wire causes the motor to stop
automatically (safe design).
• When you configure the inverter for 3-wire
interface control, the dedicated [FW] terminal is
automatically disabled. The [RV] intelligent
terminal assignment is also disabled.
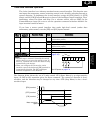
Example (default input configuration shown—see
page 3–49):
See I/O specs on page 4–6.
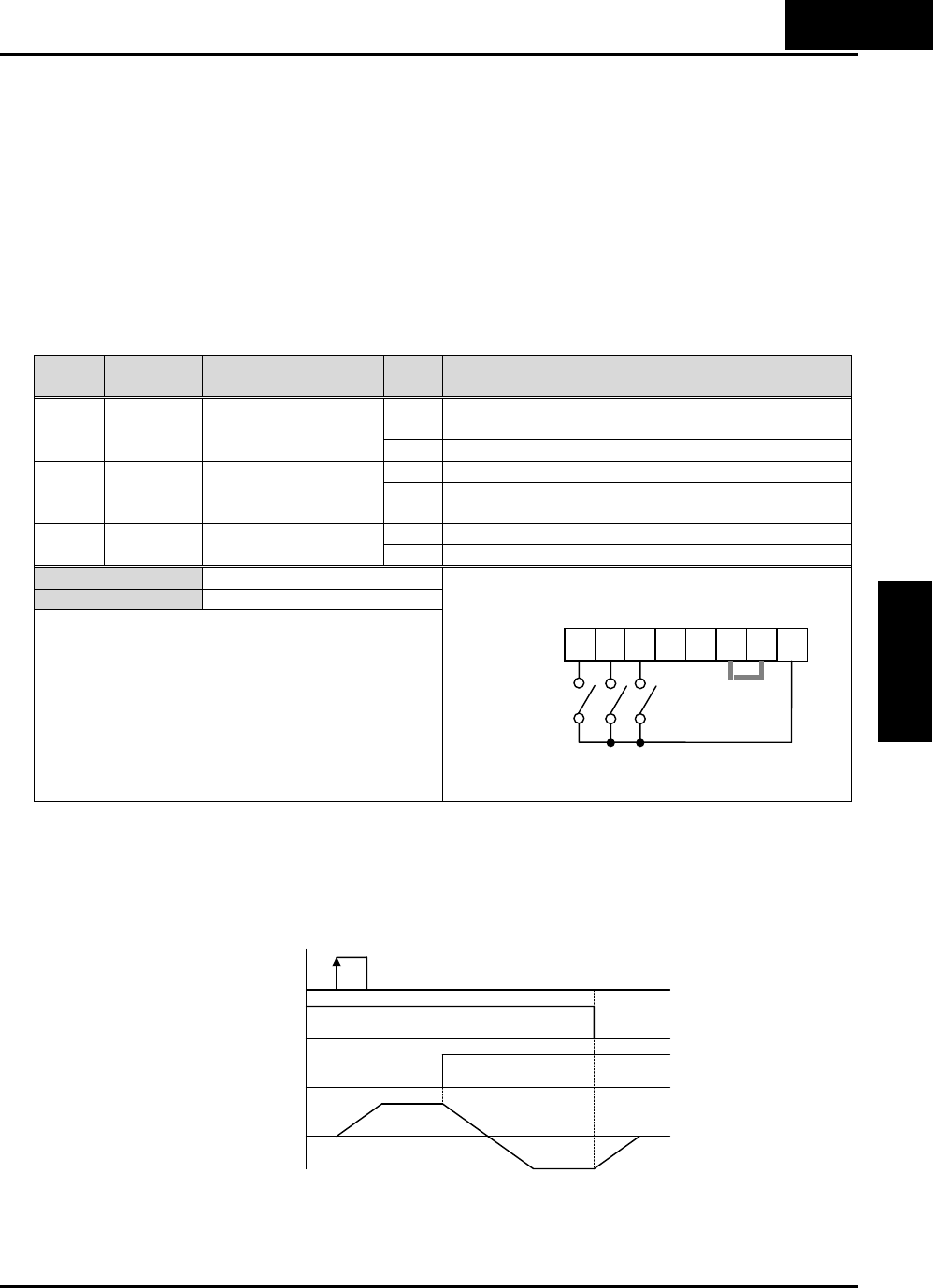
The diagram below shows the use of 3-wire control. STA (Start Motor) is an edge-sensitive
input; an OFF-to-ON transition gives the Start command. The control of direction is level-
sensitive, and the direction may be changed at any time. STP (Stop Motor) is also a level-
sensitive input.
5 4 3 2 1 L
PCS
P24
F/R
STA
STP
[STP] terminal
1
0
t
[F/R] terminal
1
0
Motor revolution
speed
[STA] terminal
1
0
4
−
25
Operations and
Monitoring