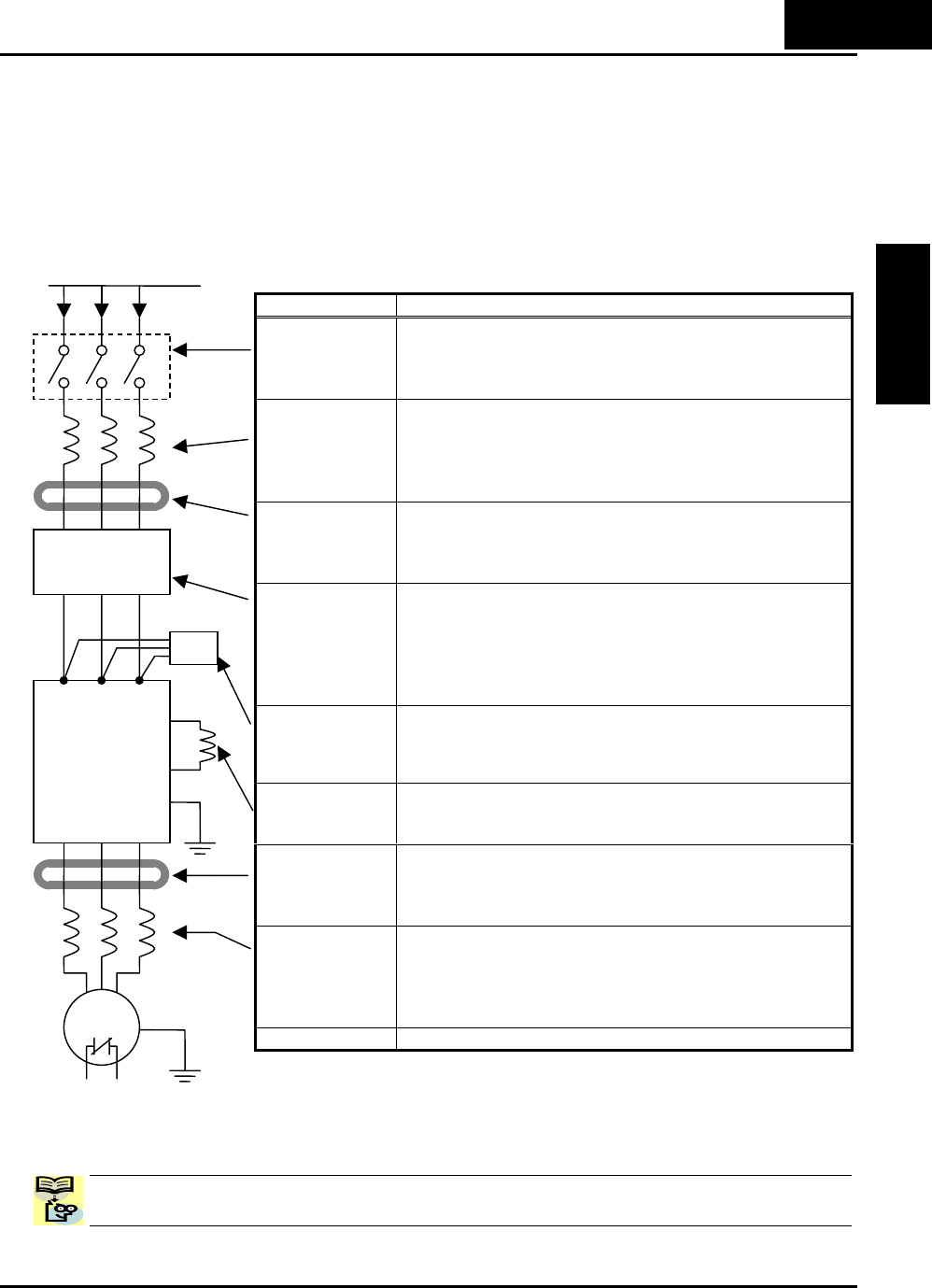
Basic System Description
A motor control system will obviously include a motor and inverter, as well as a breaker
or fuses for safety. If you are connecting a motor to the inverter on a test bench just to
get started, that’s all you may need for now. But a system can also have a variety of
additional components. Some can be for noise suppression, while others may enhance
the inverter’s braking performance. The figure and table below show a system with all
the optional components you may need in your finished application.
Name Function
Breaker /
disconnect
A molded-case circuit breaker (MCCB), ground fault
interrupter (GFI), or a fused disconnect device. NOTE:
The installer must refer to the NEC and local codes to
ensure safety and compliance.
Input-side
AC Reactor
This is useful in suppressing harmonics induced on the
power supply lines and for improving the power factor.
WARNING: Some applications
must
use an input-side
AC Reactor to prevent inverter damage. See Warning on
next page.
Radio noise
filter
Electrical noise interference may occur on nearby
equipment such as a radio receiver. This magnetic choke
filter helps reduce radiated noise (can also be used on
output).
EMI filter (for
CE applications,
see Appendix D)
Reduces the conducted noise on the power supply wiring
between the inverter and the power distribution system.
Connect to the inverter primary (input) side.
EU version (with a suffix of -FEF have integrated EMC
Filter, which is category C1 for 200V class and C2 for
400V class.)
Radio noise
filter (use in
non-CE
applications)
This capacitive filter reduces radiated noise from the
main power wires in the inverter input side.
DC link choke
Suppress harmonics generated by the inverter.
However, it will not protect the input diode bridge
rectifier.
Radio noise
filter
Electrical noise interference may occur on nearby
equipment such as a radio receiver. This magnetic choke
filter helps reduce radiated noise (can also be used on
input).
Output-side
AC Reactor
This reactor reduces the vibration in the motor caused
by the inverter’s switching waveforms, by smoothing the
waveform to approximate commercial power quality. It
is also useful to reduce harmonics when wiring from the
inverter to the motor is more than 10m in length.
LCR filter
Sine wave shaping filter for output side.
NOTE: Note that some components are required for regulatory agency compliance (see
Chapter 5 and Appendix D).
Breaker,
MCCB or
GFI
From power supply
Motor
Thermal
switch
L1 L2 L3
T1 T2 T3
Inverter
+1
+
GND
2
−
7
Inverter Mounting
and installation


















