Vol. 2A 2-1
CHAPTER 2
INSTRUCTION FORMAT
This chapter describes the instruction format for all Intel 64 and IA-32 processors.
The instruction format for protected mode, real-address mode and virtual-8086
mode is described in Section 2.1. Increments provided for IA-32e mode and its sub-
modes are described in Section 2.2.
2.1 INSTRUCTION FORMAT FOR PROTECTED MODE,
REAL-ADDRESS MODE, AND VIRTUAL-8086 MODE
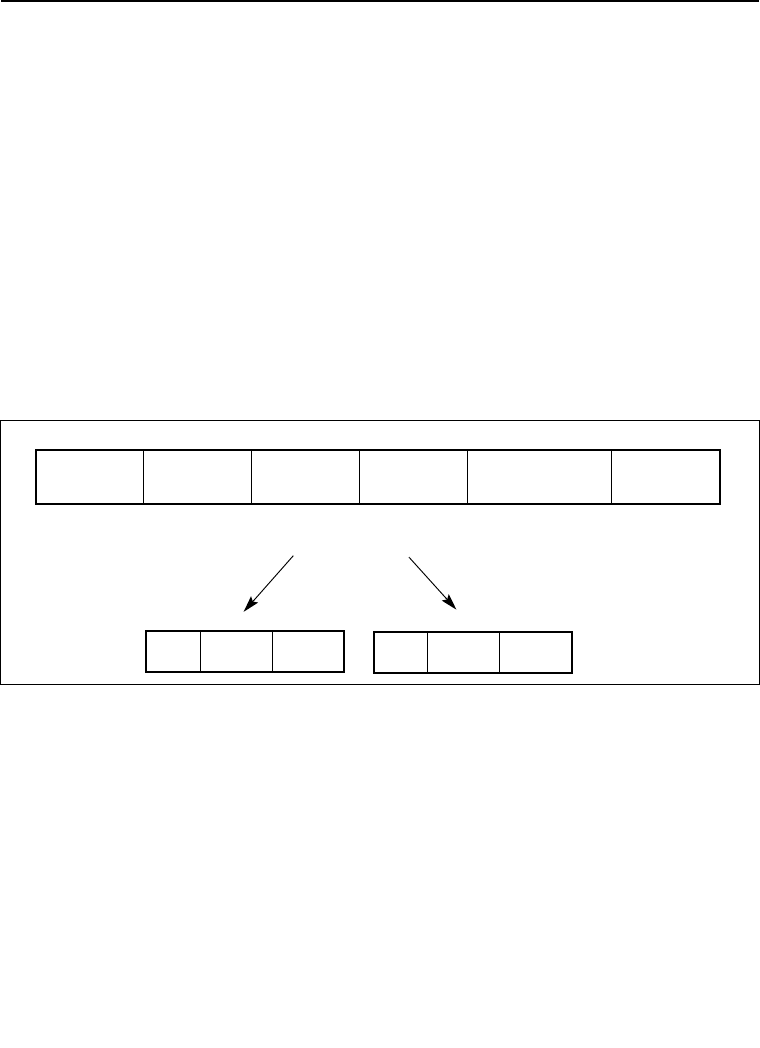
The Intel 64 and IA-32 architectures instruction encodings are subsets of the format
shown in Figure 2-1. Instructions consist of optional instruction prefixes (in any
order), primary opcode bytes (up to three bytes), an addressing-form specifier (if
required) consisting of the ModR/M byte and sometimes the SIB (Scale-Index-Base)
byte, a displacement (if required), and an immediate data field (if required).
2.1.1 Instruction Prefixes
Instruction prefixes are divided into four groups, each with a set of allowable prefix
codes. For each instruction, one prefix may be used from each of four groups (Groups
1, 2, 3, 4) and be placed in any order.
• Group 1
— Lock and repeat prefixes:
• F0H—LOCK
Figure 2-1. Intel 64 and IA-32 Architectures Instruction Format
Instruction
Prefixes
Opcode
ModR/M
SIB Displacement
Immediate
Mod
R/M
Reg/
Opcode
0
2
7
65
3
Scale
Base
0
27
65 3
Index
Immediate
data of
1, 2, or 4
bytes or none
Address
displacement
of 1, 2, or 4
bytes or none
1 byte
(if required)
1 byte
(if required)
1-, 2-, or 3-byte
opcode
Up to four
prefixes of
1 byte each
(optional)
