power supply configurations. The base DC-powered router includes the midplane,
craft interface, and fan tray running at normal speed.
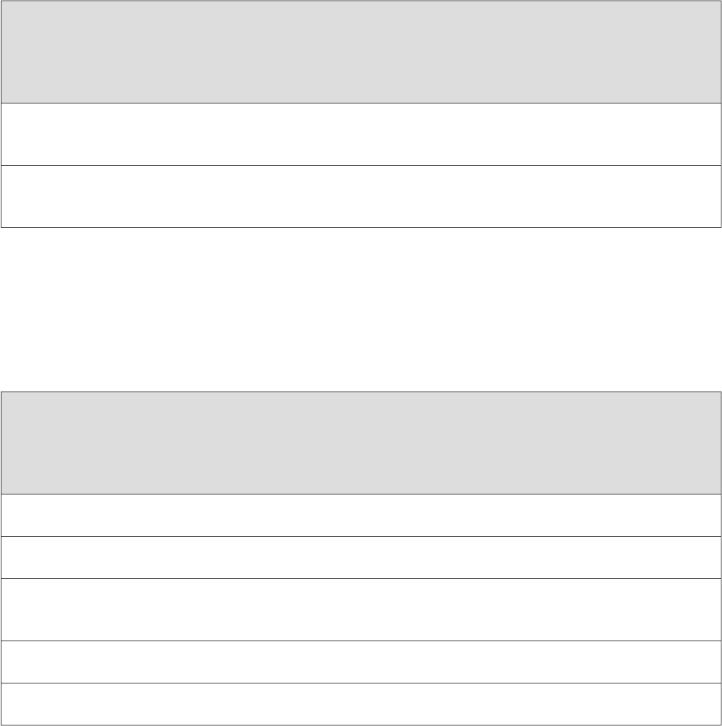
Table 30: DC-Powered Base Router Power Requirements
Current
Requirement
(Amps @
–48 VDC)
Power
Requirement
(Watts)DC Power Supply Configuration
1.04 A
(approximate)
50 W
(approximate)
One DC power supply (nonredundant configuration)
1.38 A
(approximate)
66 W
(approximate)
Two DC power supplies (redundant configuration)
Table 31 on page 168 lists the power requirements for various hardware components
when the router is operating under typical voltage conditions.
Table 31: Component Power Requirements
Current
Requirement
(Amps @
–48 VDC)Power Requirement (Watts)Component
3.1 A150 WSCB
1.9 A90 WRouting Engine
0.4 A70 W – 50 W = 20 WFan tray (full speed) – Fan tray (normal
speed)
6.5 A312 WDPC—Generalized typical value
7.6 A365 WDPC—Generalized maximum value
These examples use generalized values for DPCs. For DPC power requirements, see
the MX-series Ethernet Services Router DPC Guide.
Typical power consumption for DC-powered routers:
■ Minimum DC-powered configuration:
Base router (with fan tray at normal speed and one power supply) + 1 SCB + 1
Routing Engine + 1 DPC =
1.04 A +3.1 A + 1.9 A + 6.5 A = 12.5 A @ –48 VDC = 600.0 W DC
■ Maximum DC-powered configuration with one host subsystem and a third DPC
in the multifunction slot:
Base router and two power supplies + fan tray at full speed + 1 SCB + 1 Routing
Engine + 3 DPCs
168 ■ DC Power Specifications and Requirements
MX240 Ethernet Services Router Hardware Guide