Calculating Power Budget for Fiber-Optic Cable
To ensure that fiber-optic connections have sufficient power for correct operation,
calculate the link's power budget, which is the maximum amount of power it can
transmit. When you calculate the power budget, you use a worst-case analysis to
provide a margin of error, even though all the parts of an actual system do not operate
at the worst-case levels. To calculate the worst-case estimate of power budget (P
B
),
you assume minimum transmitter power (P
T
) and minimum receiver sensitivity (P
R
):
P
B
= P
T
– P
R
The following hypothetical power budget equation uses values measured in decibels
(dB) and decibels referred to one milliwatt (dBm):
P
B
= P
T
– P
R
P
B
= –15 dBm – (–28 dBm)
P
B
= 13 dB
Calculating Power Margin for Fiber-Optic Cable
After calculating a link's power budget (using the equation described in “Calculating
Power Budget for Fiber-Optic Cable” on page 181), you can calculate the power margin
(P
M
), which represents the amount of power available after subtracting attenuation
or link loss (LL) from the power budget (P
B
). A worst-case estimate of P
M
assumes
maximum LL:
P
M
= P
B
– LL
A P
M
greater than zero indicates that the power budget is sufficient to operate the
receiver.
Factors that can cause link loss include higher-order mode losses, modal and
chromatic dispersion, connectors, splices, and fiber attenuation. Table 38 on page
181 lists an estimated amount of loss for the factors used in the following sample
calculations. For information about the actual amount of signal loss caused by
equipment and other factors, refer to vendor documentation.
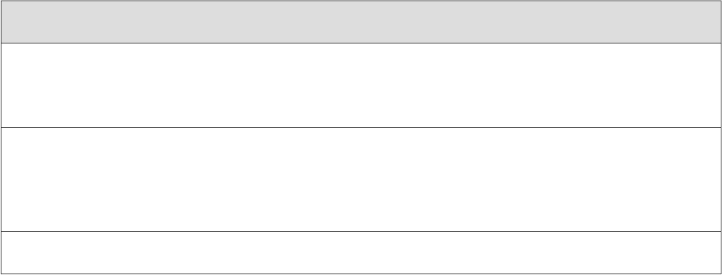
Table 38: Estimated Values for Factors Causing Link Loss
Estimated Link-Loss ValueLink-Loss Factor
Single-mode—None
Multimode—0.5 dB
Higher-order mode losses
Single-mode—None
Multimode—None, if product of bandwidth and distance
is less than 500 MHz–km
Modal and chromatic dispersion
0.5 dBConnector
Network Cable Specifications and Guidelines ■ 181
Appendix E: Cable and Wire Guidelines and Specifications


















