13 - 25
13. OPTIONS AND AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT
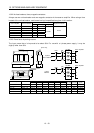
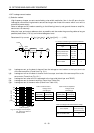
(b) Reduction techniques for external noises that cause the servo amplifier to malfunction
If there are noise sources (such as a magnetic contactor, an electromagnetic brake, and many
relays which make a large amount of noise) near the servo amplifier and the servo amplifier may
malfunction, the following countermeasures are required.
Provide surge absorbers on the noise sources to suppress noises.
Attach data line filters to the signal cables.
Ground the shields of the encoder connecting cable and the control signal cables with cable clamp
fittings.
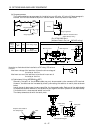
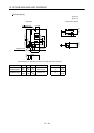
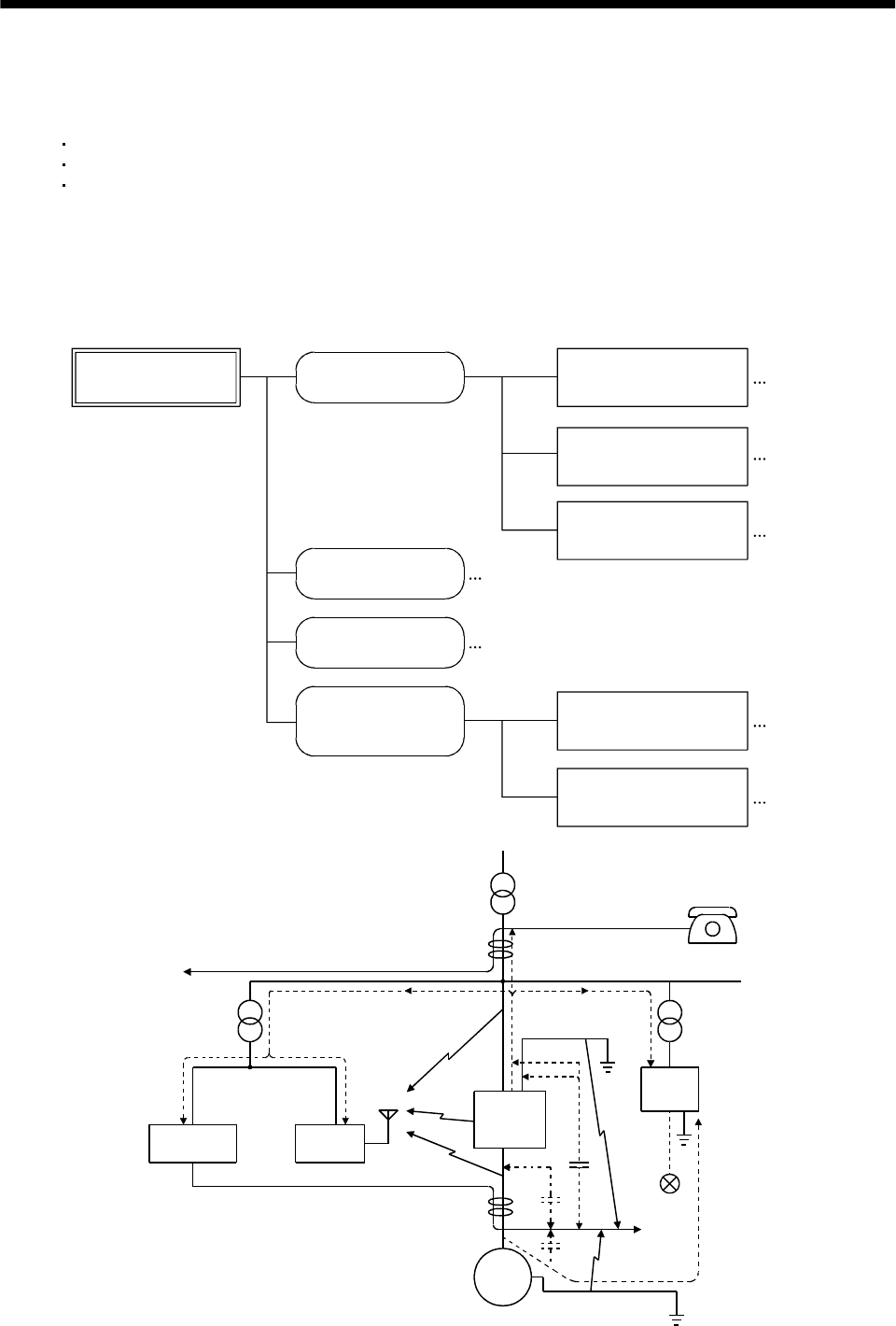
(c) Techniques for noises radiated by the servo amplifier that cause peripheral devices to malfunction
Noises produced by the servo amplifier are classified into those radiated from the cables connected
to the servo amplifier and its main circuits (input and output circuits), those induced
electromagnetically or statically by the signal cables of the peripheral devices located near the
main circuit cables, and those transmitted through the power supply cables.
Noises produced
by servo amplifier
Noises transmitted
in the air
Noise radiated directly
from servo amplifier
Magnetic induction
noise
Static induction
noise
Noises transmitted
through electric
channels
Noise radiated from the
power supply cable
Noise radiated from
servo motor cable
Noise transmitted through
power supply cable
Noise sneaking from
grounding cable due to
leakage current
Routes 4) and 5)
Route 1)
Route 2)
Route 3)
Route 7)
Route 8)
Route 6)
Instrument Receiver
Servo
amplifier
Servo motor SM
2)
2)
8)
1)
7)
7) 7)
5)
3)
4)
6)
3)
Sensor
power
supply
Sensor