14 - 8
14. SERVO MOTOR
14.4.4 Permissible load for the shaft
POINT
Do not use a rigid coupling as it may apply excessive bending load to the
shaft, leading to shaft breakage.
(a) Use a flexible coupling and make sure that the misalignment of the shaft is less than the
permissible radial load.
(b) When using a pulley, sprocket or timing belt, select a diameter that will fit into the permissible
radial load.
(c) Excess of the permissible load can cause the bearing life to reduce and the shaft to break.
(d) The load indicated in this section is static load in a single direction and does not include eccentric
load. Make eccentric load as small as possible. Not doing so can cause the servo motor to be
damaged.
(1) Without reduction gear
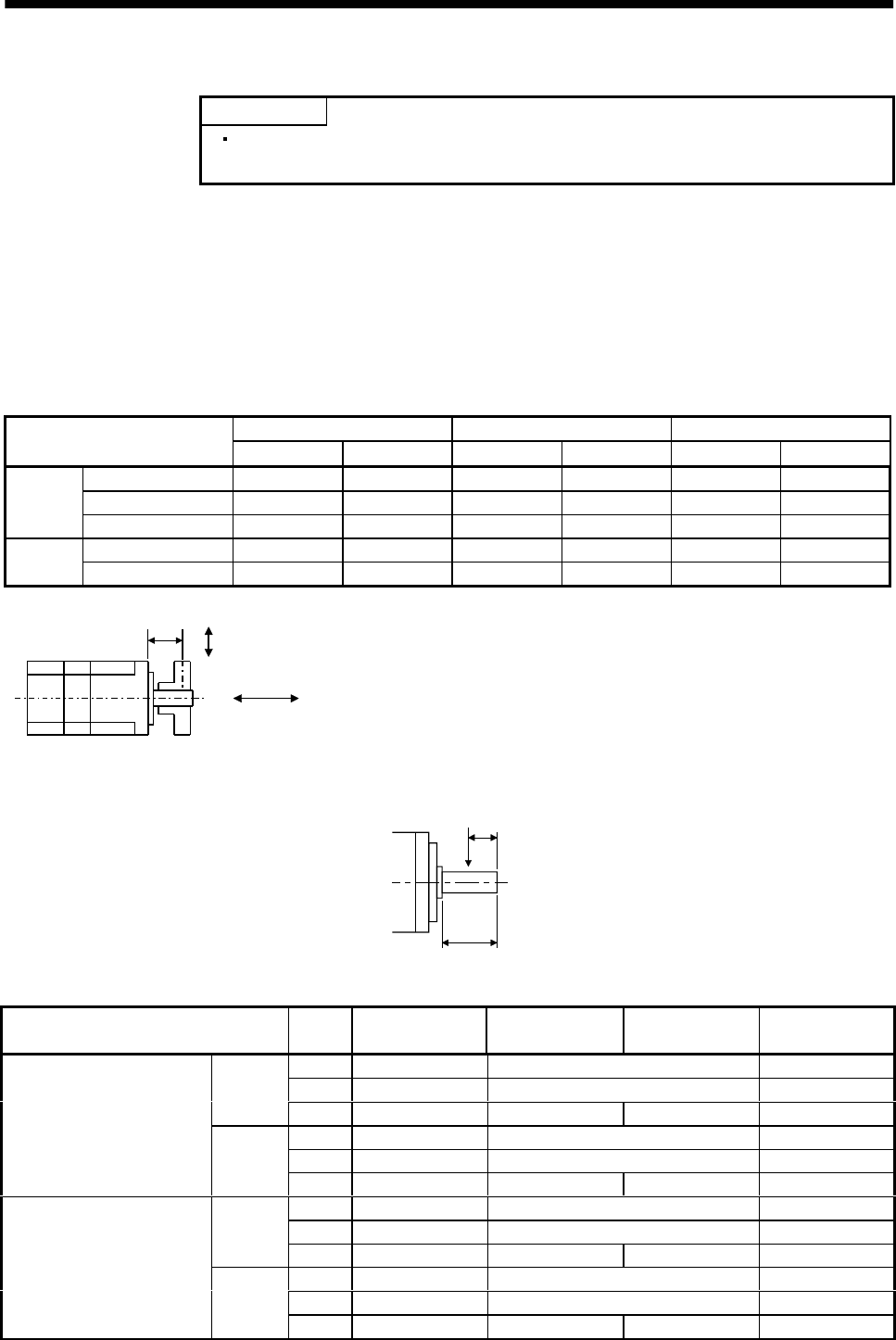
(Note ) L Permissible Radial Load Permissible Thrust Load
Servo Motor
[mm] [in] [N] [lb] [N] [lb]
053 / 13 25 0.98 88 20 59 13
23 / 43 30 1.18 245 55 98 22HC-KFE
73 40 1.57 392 88 147 33
52 to 152 55 2.17 980 220 490 110
HC-SFE
202 79 3.11 2058 463 980 220
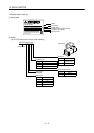
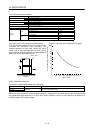
Note : For the symbols in the table, refer to the following diagram:
Radial load
Thrust load
L
L: Distance from flange mounting surface to load center
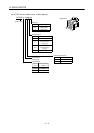
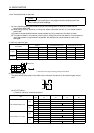
(2) With reduction gear
The permissible radial loads in the table are the values at the center of the reduction gear output
shaft.
Q/ 2
Q
(a) HC-KFE series
1) General industrial machine-compliant
Item
Gear
ratio
HC-KFE13(B)
G1
HC-KFE23(B)
G1
HC-KFE43(B)
G1
HC-KFE73(B)
G1
1/5 150 330 430
1/12 240 710 620
[N]
1/20 370 780 760 970
1/5 34 74 97
1/12 54 160 139
Permissible Radial Load
[lb]
1/20 83 175 171 218
1/5 200 350 430
1/12 320 720 620[N]
1/20 450 780 760 960
1/5 45 79 97
1/12 72 162 139
Permissible Thrust Load
[lb]
1/20 101 175 171 216