103
2
2) PD action
A combination of proportional control
action (P) and differential control
action (D) for providing a manipulated
variable in response to deviation
speed to improve the transient
characteristic.
REMARKS
PD action is the sum of P and D actions.
[Operation example for proportional changes
of process value]
Deviation
Set point
Time
Time
Time
PD action
D action
P action
Process
value
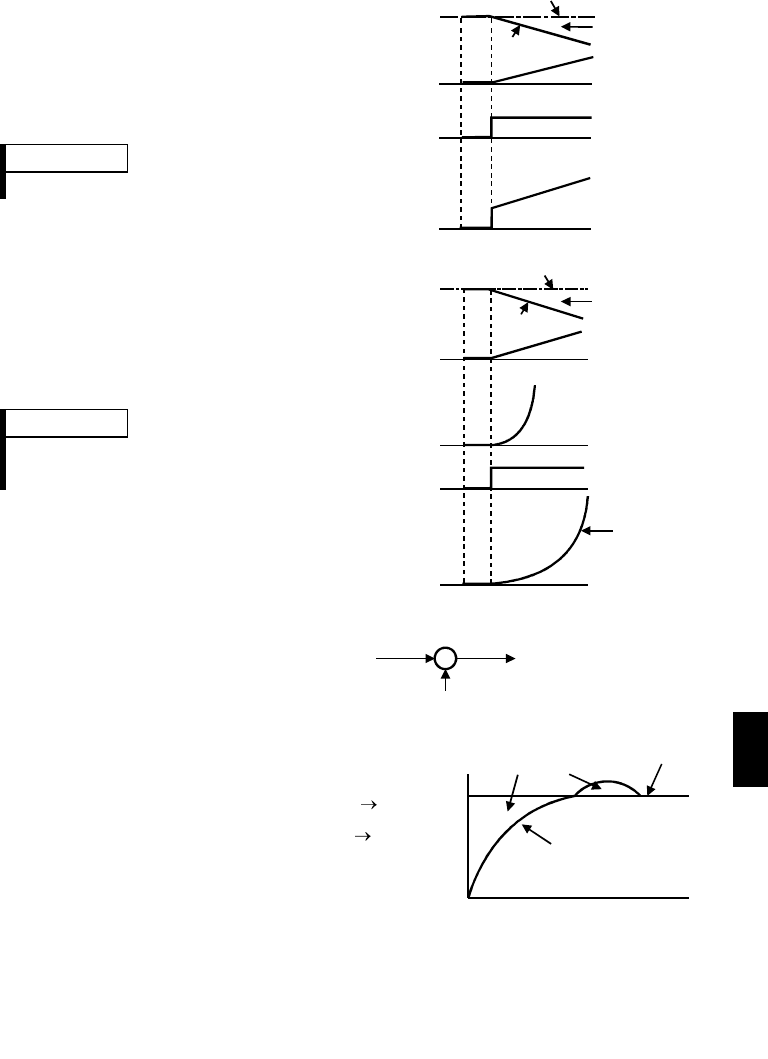
3) PID action
The PI action and PD action are
combined to utilize the advantages of
both actions for control.
REMARKS
The PID action is the sum of P, I and D
actions.
Time
Time
Time
Deviation
P action
D action
PID action
Set point
Process
value
Time
I action
y=at +bt+
c
2
4) Reverse action
Increases the manipulated
variable (output frequency) if
deviation X = (set point -
process value) is positive,
and decreases the
manipulated variable if
deviation is negative.
Set point
Feedback signal
(Process value)
+
-
[Heating]
Deviation
Set point
X>0
X<0
Cold up
Hot down
Process value


















