104
5) Forward action
Increases the manipulated
variable (output frequency) if
deviation X = (set point -
process value) is negative,
and decreases the
manipulated variable if
deviation is positive.
Set point
X>0
X<0
Feedback signal
(Process value)
+
-
[Cooling]
Too cold down
Hot up
Set point
Process value
Deviation
Relationships between deviation and manipulated variable (output frequency)
Deviation
Positive Negative
Reverse action
!"
Forward action
"!
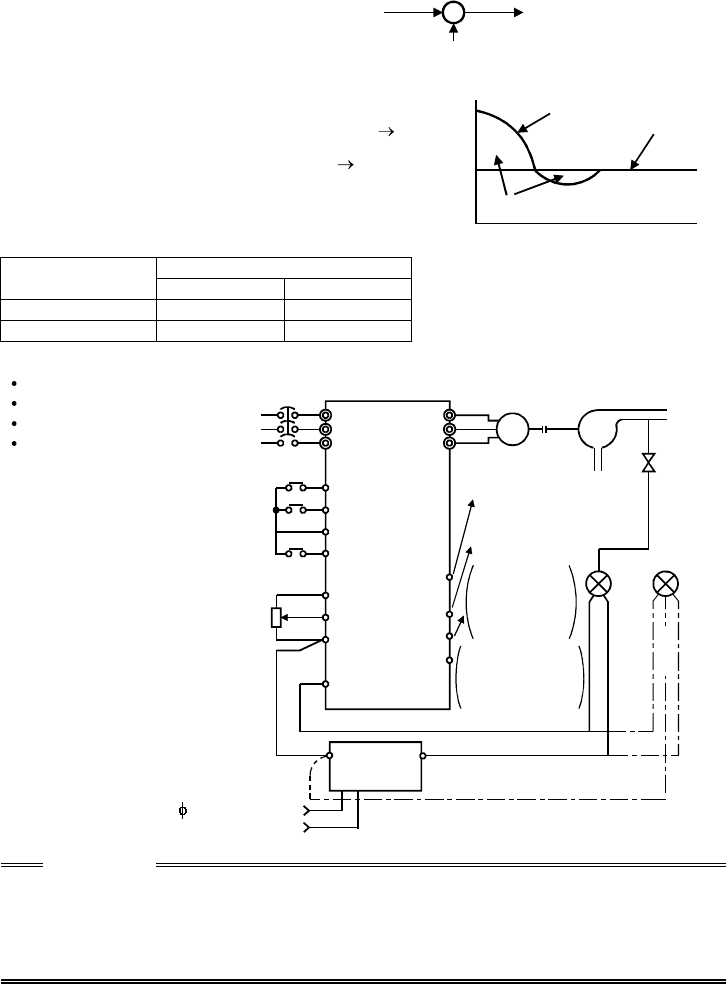
(3) Wiring example
Pr. 60 = 14
Pr. 64 = 15
Pr. 65 = 16
Pr. 88 = 20
Limit signal
common
For
2-wire
type
Detector
Motor
Power
supply
NFB
Inverter
0 24V
DC
power supply
(*1)
R(L
1
)
S(N)
T
STF
STR
SD
10
2
5
4
U
V
W
SE
(Process value) 4 to 20mA
IM
P
-
+
++
-
(OUT)
(24V)
A
C
RUN(FUP,FDN)
PID control
selection
RL(X14)(*3)
(*2)
Forward rotation
Reverse rotation
Setting
potentiometer
(Set point setting)
Pump
For
3-wire
type
Upper limit
(Lower limit)
Forward (reverse)
rotation output
signal common
Forward
rotation output
Reverse
rotation output
AC1
200/220V 50/60Hz
(COM)
CAUTION
*1. The power supply must be selected in accordance with the power specifications
of the detector used.
*2. The output signal terminals used depends on the Pr. 64, Pr. 65 settings.
*3. The input signal terminal used depends on the setting of Pr. 60 to Pr. 63.
• The contact input signal (AU Signal) need not be turned on.


















