RuggedRouter® User Guide
Each Virtual Router has a user-configured Virtual Router Identifier (VRID) and an
Virtual IP address or set of IP addresses on the shared LAN. Hosts on the shared
LAN are configured to use these addresses as the default gateway.
One router in the Virtual Router Group will be elected as the Master, all other routers
in the group will be Backups.
Each router in the group will run at a specific Priority. The router with the highest
priority is elected Master. The value of Priority varies from 1 to 255.
VRRP can also monitor a specified interface and give up control of a VRIP if that
interface goes down.
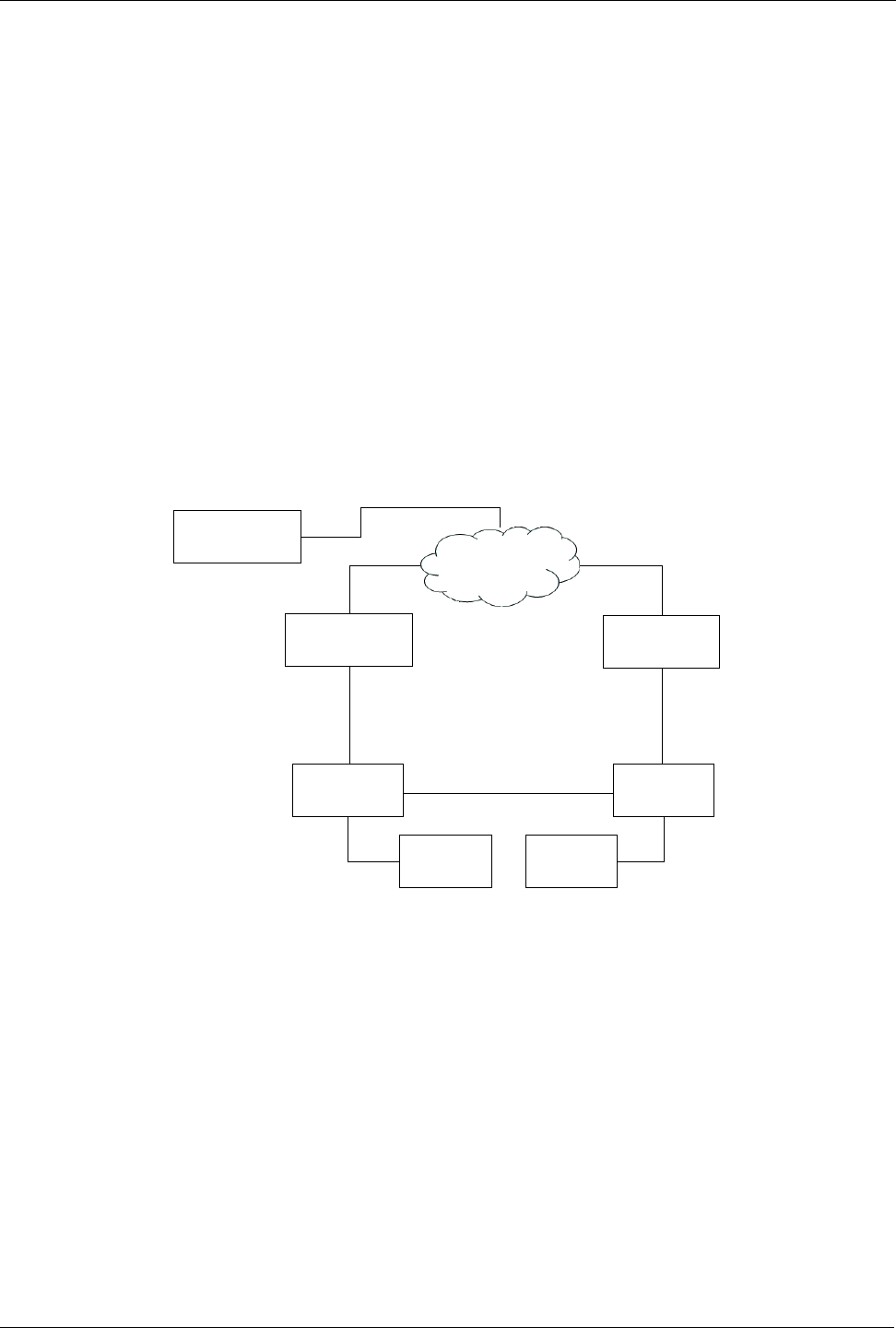
In the following network, host 1 uses a gateway of 1.1.1.253 and host 2 uses a
gateway of 1.1.1.252. The 1.1.1.253 gateway is provided by VRID 10. In normal
practice router 1 will provide this virtual IP as its priority for VRID 10 is higher than
that of router 2. If router 1 becomes inoperative or if its w1ppp link fails, it will
relinquish control of VRIP 1.1.1.253 to router 2.
In a similar fashion host 2 can use the VRID 11 gateway address of 1.1.1.252 which
will normally be supplied by router 2.
Figure 151: VRRP Example
In this example traffic from host1 will be sent through router 1 and traffic from host2
through router 2. A failure of either router (or its wan link) will be recovered by the
other router.
Note that both routers can always be reached by the hosts at their “real” IP addresses.
Two or more VRRP instances can be assigned to be in the same VRRP Group, in
which case, they can failover together.
176 RuggedCom
Remote
Router 2
Remote
Router 1
w2ppp
w1ppp
1.1.1.200
SwitchSwitch
Host 1
VRID 10 VRIP = 1.1.1.253
VRID 10 Priority = 100
VRID 10 Monitor w1ppp
VRID 11 VRIP = 1.1.1.252
VRID 11 Priority = 50
VRID 10 VRIP = 1.1.1.253
VRID 10 Priority = 50
VRID 11 VRIP = 1.1.1.252
VRID 11 Priority = 100
VRID 11 Monitor w2ppp
Host 2
1.1.1.201
Central Site
Network


















