20060301
(9) Tap [OK].
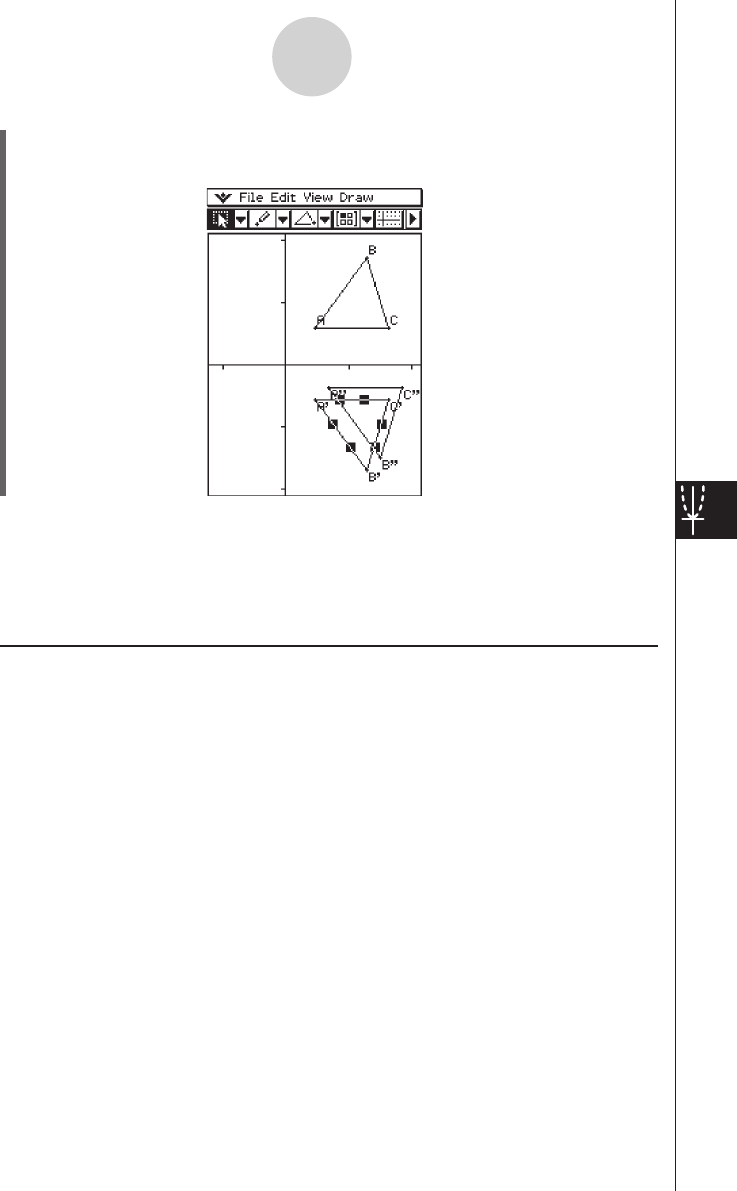
• This performs the parallel displacement and draws triangle A’’B’’C’’.
Note
• In the above example, we performed the transformation and the parallel displacement
operations separately. You could also perform both operations at the same time, if you
want. To do so, input both the matrix [[1, 0], [0,
–
1]] and the vector [1, 1] in step (4), and
then tap [OK]. This will produce the result shown in step (9).
k
Transform Example Using the Main Application
It might be easier to understand how General Transform works if you use the Main
application (or eActivity application) in combination with the Geometry application. This
makes it possible to perform the following types of operations.
(a) In the Geometry application, you can select a point on the figure obtained using
General Transform and the corresponding point on the original figure (for example,
point A on the original figure and point A’ on the transformed figure), drag them to the
Main application, and display the transformation expression in the Main application.
(b) You can select a triangle in the Geometry application and drag it to the Main
application to convert the triangle to a matrix (2-row
×
3-column matrix that shows three
vertices). Conversely, you can drag a 2-row
×
3-column matrix input (or produced by a
calculation) in the Main application to the Geometry application and draw the applicable
triangle.
Here we will show actual examples of (a) and (b).
Tip
• All of the above operations can also be performed using the eActivity application instead of the
Main application.
• For information about how to access the Geometry application from the Main application
and about the different operations you can perform between them, see “2-10 Using the Main
Application in Combination with Other Applications”.
8-2-40
Drawing Figures


















