Rev. 1.00, 05/04, page 257 of 544
Table 12.9 SSR Status Flags and Receive Data Handling
SSR Status Flag
RDRF* ORER FER PER
Receive Data Receive Error Type
1 1 0 0 Lost Overrun error
0 0 1 0 Transferred to RDR Framing error
0 0 0 1 Transferred to RDR Parity error
1 1 1 0 Lost Overrun error + framing error
1 1 0 1 Lost Overrun error + parity error
0 0 1 1 Transferred to RDR Framing error + parity error
1 1 1 1 Lost Overrun error + framing error
+ parity error
Note: * The RDRF flag retains the state it had before data reception.
Yes
<End>
[1]
No
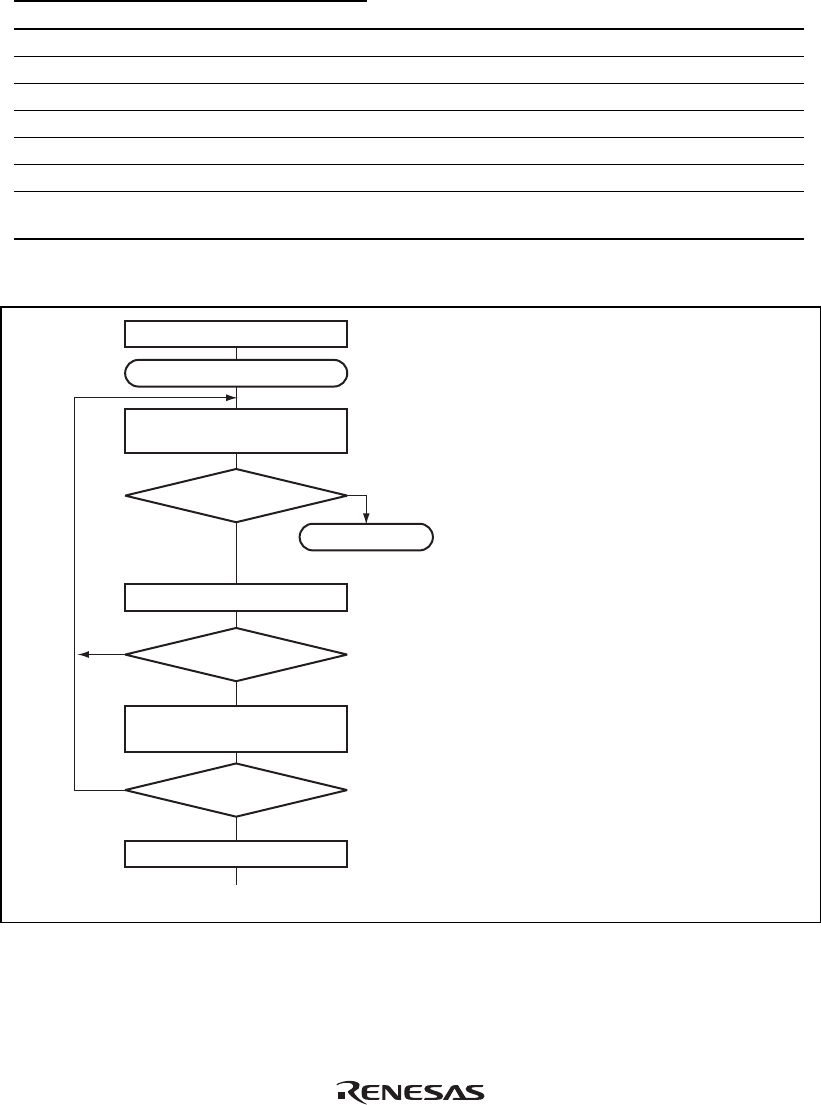
Initialization
Start reception
[2]
No
Yes
Read RDRF flag in SSR
[4]
[5]
Clear RE bit in SCR to 0
Read ORER, PER, and
FER flags in SSR
Error processing
(Continued on next page)
[3]
Read receive data in RDR, and
clear RDRF flag in SSR to 0
No
Yes
PER ∨ FER ∨ ORER = 1
RDRF = 1
All data received?
[1] SCI initialization:
The RxD pin is automatically designated
as the receive data input pin.
[2] [3] Receive error processing and break
detection:
If a receive error occurs, read the ORER,
PER, and FER flags in SSR to identify the
error. After performing the appropriate
error processing, ensure that the ORER,
PER, and FER flags are all cleared to 0.
Reception cannot be resumed if any of
these flags are set to 1. In the case of a
framing error, a break can be detected by
reading the value of the input port
corresponding to the RxD pin.
[4] SCI status check and receive data read:
Read SSR and check that RDRF = 1, then
read the receive data in RDR and clear the
RDRF flag to 0. Transition of the RDRF
flag from 0 to 1 can also be identified by an
RXI interrupt.
[5] Serial reception continuation procedure:
To continue serial reception, before the
stop bit for the current frame is received,
read the RDRF flag, read RDR, and clear
the RDRF flag to 0.
[Legend]
∨ : Logical OR
Figure 12.9 Sample Serial Reception Flowchart (1)


















