Rev. 1.00, 05/04, page 357 of 544
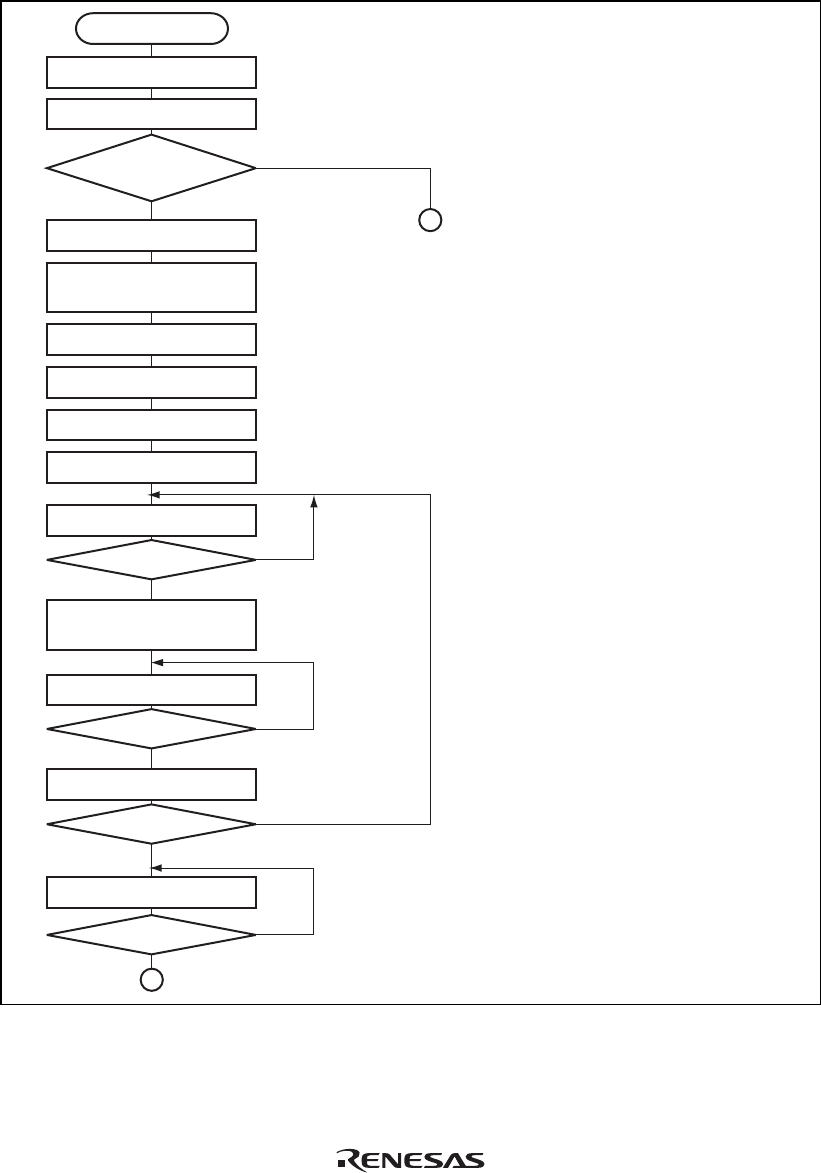
Start
Set KBIOE bit
KCLKI = 0?
Read KBCRH
KCLKI
and KDI bits both
1?
Set I/O inhibit (KCLKO = 0)
KBE = 0
(KBBR reception prohibited)
KDO remains at 1
Wait
Set start bit (KDO = 0)
Set I/O inhibit (KCLKO = 1)
KCLKO remains at 0
KDO remains at 0
i = 0
Read KBCRH
Set transmit data
(KDO = D(i))
Read KBCRH
KCLKI = 1?
i = i + 1
i > 9?
Read KBCRH
KCLKI = 1?
Yes
No
i = 0 to 7: Transmit data
i = 8: Parity bit
i = 9: Stop bit
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
1
2
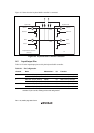
[1] Set the KBE bit to 1 in KBCRH.
[2] Read KBCRH, and if the KCLKI and KDI
bits are both 1, write 0 in the KCLKO bit
(set I/O inhibit).
[3] Write 0 in the KBE bit (prohibit KBBR
receive operation).
[4] Write 0 in the KDO bit (set start bit).
[5] Write 1 in the KCLKO bit (clear I/O inhibit).
[6] Read KBCRH, and when KCLKI = 0, set
the transmit data in the KDO bit (LSB-
first). Next, set the parity bit and stop bit in
the KDO bit.
[7] After transmitting the stop bit, read KBCRL
and confirm that KDI = 0 (receive
completed notification from the keyboard).
[8] Read KBCRH. Confirm that the KCLKI
and KDI bits are both 1.
The transmit operation can be continued by
repeating steps [2] to [8].
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
(Continued on
next page)
(Continued on next page)
Figure 14.5 Sample Transmit Processing Flowchart (1)