Using GPS 53
Using GPS
Mobile-Originated Service Modes
There are two modes of mobile-originated GPS service. Some devices support only one
mode; others support both.
●
Basic – the default mode of all GPS-capable mobile broadband devices. In this
mode, the Sprint network helps the device to obtain its initial fix on GPS satellites.
This has the effect of allowing the device to obtain its initial position reading
somewhat faster than in stand-alone mode. However, this mode requires access to
the Sprint network. When the Sprint network is not available, Sprint SmartView will
offer to switch to standalone mode (if your device supports it).
●
Autonomous/Standalone – in this mode, your mobile broadband device acts as a
completely standalone GPS receiver. It does not query the Sprint network for location
data. This has the advantage of being available when you are roaming, but it may
take longer to obtain initial position data from the device.
Note: If your device supports both modes, you can specify which mode will be used by default using the
GPS Mode setting on the Location/GPS tab of the Settings window.
Enabling and Disabling GPS
Using the GPS receiver in your mobile broadband device requires that you enable GPS in
the Sprint SmartView application. Using external third-party GPS applications requires that
you enable NMEA.
Enabling GPS
GPS will be enabled automatically if you do any of the following:
● Initia
te a search using the GPS Search menu
● At
tempt to launch an application using the GPS Applications menu
● Enable NME
A
Enabling NMEA
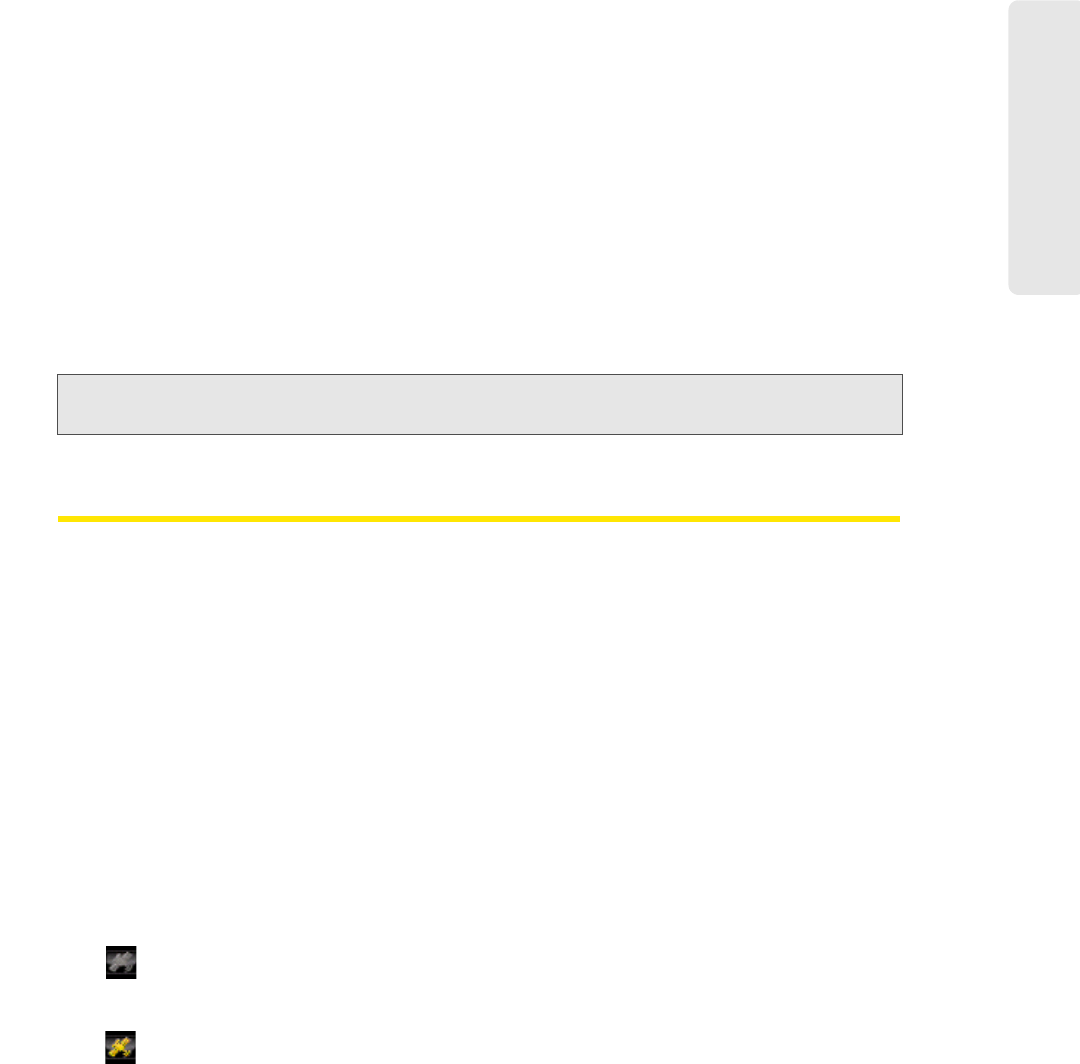
When NMEA is disabled, the GPS icon will appear gray or yellow as shown below:
(gray)
GPS and NMEA disabled. In this state, GPS data is not received by the Sprint
SmartView application.
(yellow)
GPS enabled/NMEA disabled. In this state, GPS data is received by the Sprint
SmartView application, but the received data is not shared with third-party GPS
applications.


















