Using Intelligent Input Terminals
Operations
and Monitoring
4–22
Commercial
Power Source
Switching
The commercial power source switching function is useful in systems with excessive starting
torque requirements. This feature permits the motor to be started “across the line,” sometimes
called a bypass configuration. After the motor is running, the inverter takes over to control the
speed. This feature can eliminate the need to oversize the inverter, reducing cost. However,
additional hardware such as magnetic contactors will be required to realize this function. For
example, a system may require 55KW to start, but only 15KW to run at constant speed. There-
fore, a 15KW rated inverter would be sufficient when using the commercial power source
switching.
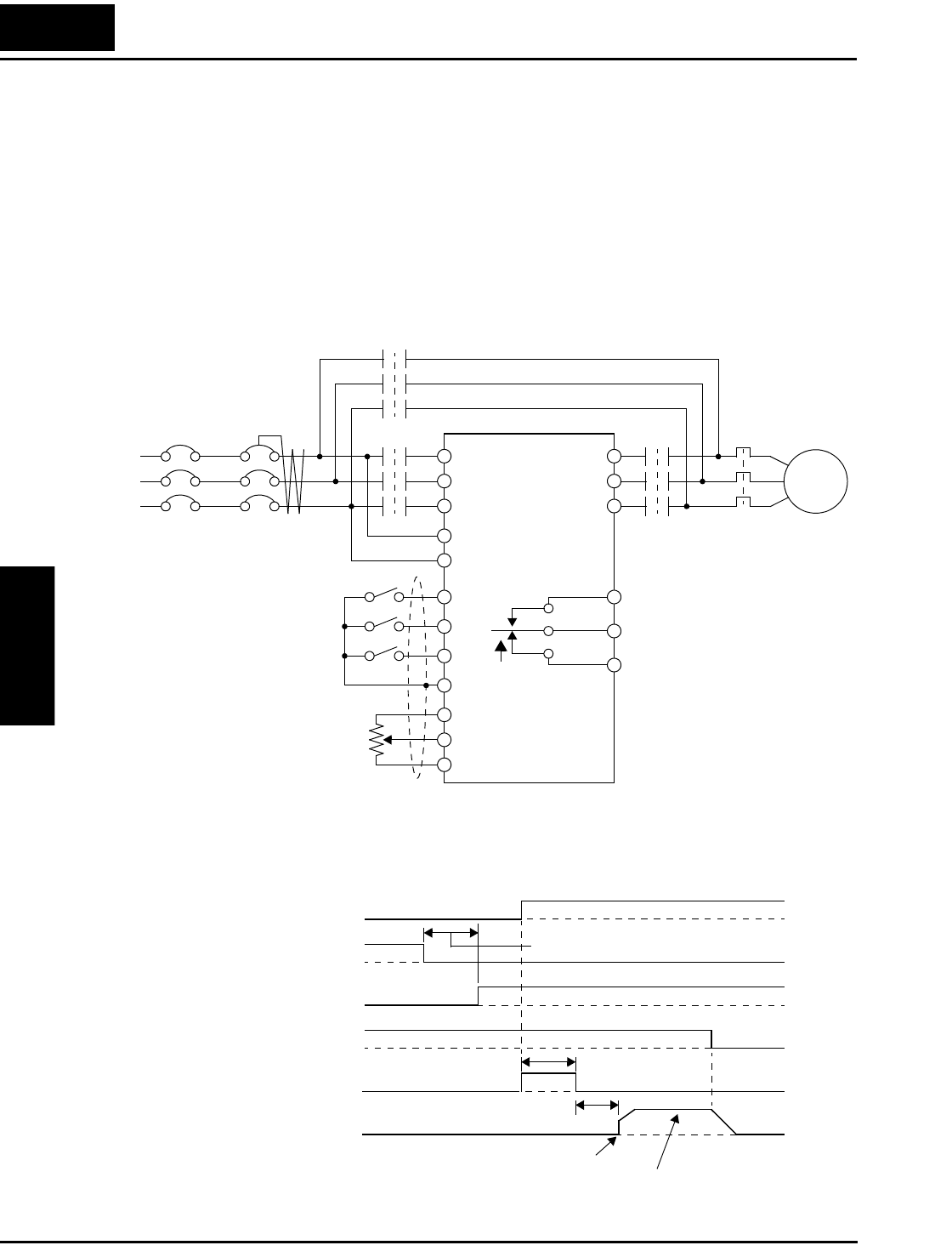
The following block diagram shows an inverter system with bypass capability. When starting
the motor directly across the line, relay contacts Mg2 are closed, and Mg1 and Mg3 are open.
This is the bypass configuration, since the inverter is isolated from the power source and motor.
Then Mg1 contacts close about 0.5 to 1 second after that, supplying power to the inverter.
Switching to inverter control occurs after the motor is running at full speed. First, Mg2 relay
contacts open. Then about 0.5 to 1 seconds later, relay Mg3 contacts close, connecting the
inverter to the motor. The following timing diagram shows the event sequence:
U
V
W
Motor
R
S
T
R0
T0
L300P
H
O
L
FW
[RV]
[CS]
CM1
Mg3
MCCB
Mg1
GFI
Mg2
Thermal
switch
Power source, 3-phase
AL0
AL2
AL1
Mg1
Mg2
Mg3
FW
[CS]
Mg2/Mg3 delay time 0.5 to 1 sec.
Set to 0.5 to 1 sec typical
Frequency matching
Inverter
output
Normal operation
B003 (Retry wait time
before motor restart)
t