252 Microarchitecture for AMD Athlon™ 64 and AMD Opteron™ Processors Appendix A
25112 Rev. 3.06 September 2005
Software Optimization Guide for AMD64 Processors
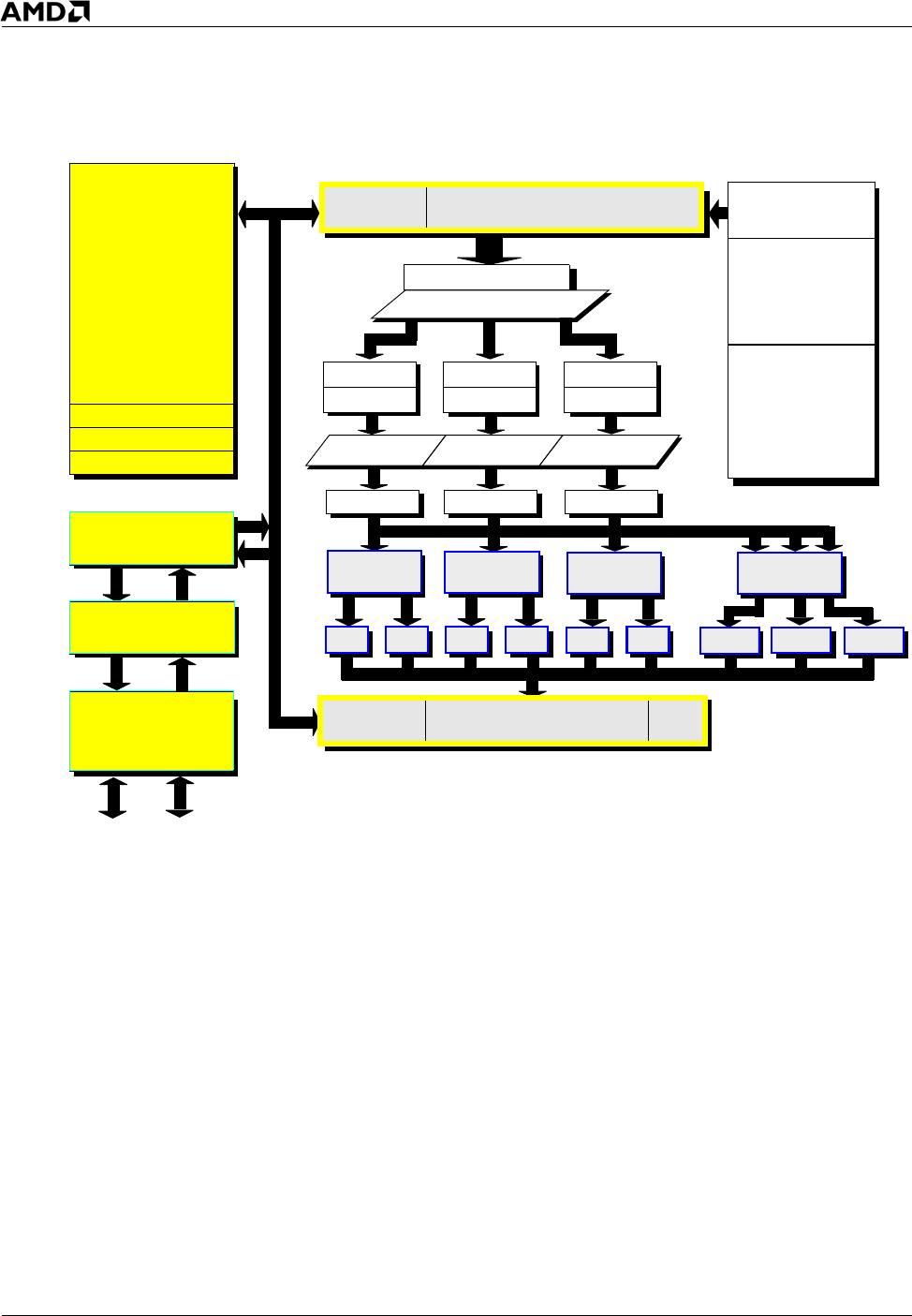
Figure 6. AMD Athlon™ 64 and AMD Opteron™ Processors Block Diagram
A.5 L1 Instruction Cache
The out-of-order execution engine of the AMD Athlon 64 and AMD Opteron processors contains a
very large L1 instruction cache. Each line in this cache is 64 bytes long. Functions associated with the
L1 instruction cache are instruction loads, instruction prefetching, instruction predecoding, and
branch prediction. Requests that miss in the L1 instruction cache are fetched from the L2 cache or,
subsequently, from the local memory using the integrated memory controller.
The L1 instruction cache generates fetches on the naturally aligned 64 bytes containing the
instructions and the next sequential line of 64 bytes (a prefetch). The principle of program-spatial
locality makes code prefetching very effective and avoids or reduces execution stalls caused by the
amount of time required to read the necessary code. Cache-line replacement is based on a least-
recently-used replacement algorithm.
Level 2
Cache
L2 ECC
L2 Tags
L2 Tag ECC
System Request
Queue (SRQ)
Cross Bar
(XBAR)
Memory Controler
and
Hypertransport
TM
Instruction
TLB
Level 1 Instruction Cache
Data
TLB
Level 1 Data Cache
Fetch 2 Transit
Target Array
and
Return Address
Branch Selectors
(4K)
Global History
Counters
Pick
Decode 1
Decode 2
Decode 1
Decode 2
Decode 1
Decode 2
Pack Pack Pack
Decode Decode DecodeDecode
8-Entry
Scheduler
8-Entry
Scheduler
8-Entry
Scheduler
36-Entry
Scheduler
AGU AGU AGUALU ALUALU
FADD FMUL FMISC
ECC
Technology
16K 2-bit
(2K Targets)
Stack
(12 Entries)