6–Configuring NIC Functionality in the Converged Network Adapter
Configuring the NIC in a Linux Environment
6-40 FE0254601-00 A
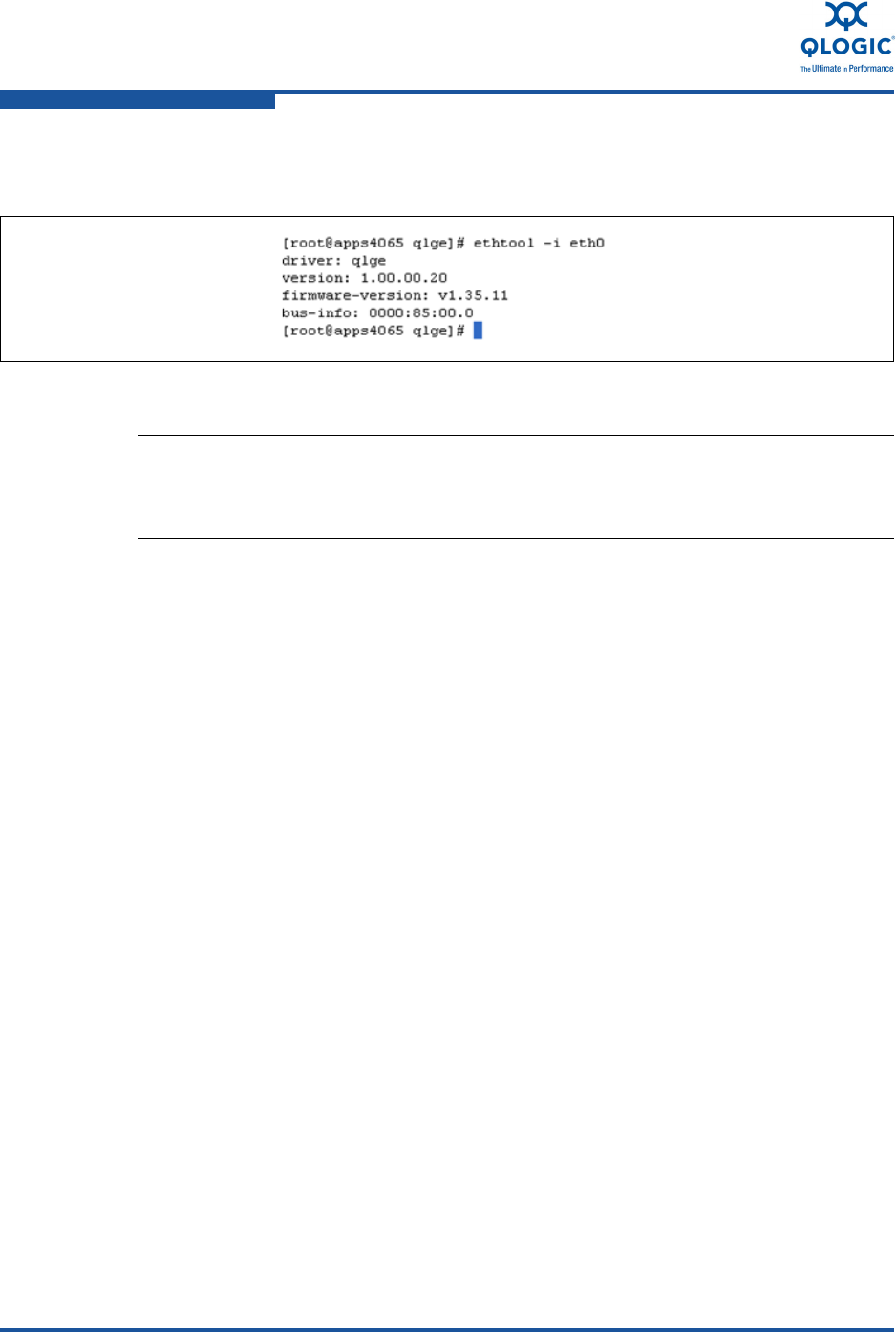
Figure 6-30 shows the sample output for the eth0 interface, associating the driver
with the interface and the location of the adapter hardware on the PCI bus.
Figure 6-30. eth0 Interface Sample Output
Interrupt Support
The QLogic 8100 Series Adapter does not support interrupt moderation.
Offload Support
The QLogic 8100 Series Adapter offloads common protocol processing onto its
hardware, which reduces host CPU processing, and increases performance. The
following types of offload are supported:
Checksum offload—The QLogic adapter supports checksum offloads for IP,
TCP (IPv4, IPv6), UDP (IPv4, IPv6) packets and the IPv4 header. Checksum
offload for these protocols is enabled by default and can be disabled using
ethtool as described in “NIC Driver Parameters (Linux)” on page 6-29. Do
not disable checksum offload unless you are debugging a checksum
computation problem. Enabling TCP checksum offload significantly reduces
host CPU processing when using jumbo frames.
Stateless offload—The QLogic 8100 Series Adapter supports large send
offloading (LSO), which enables the Linux TCP stack to send one large
block of data to the QLogic adapter, which then segments this large block
into multiple TCP packets.
NIC Bonding (Linux)
You can configure multiple QLogic 8100 Series Adapters to appear as a single
virtual network interface. This type of configuration is called teaming or trunking.
Because two or more interfaces are combined, teaming provides advantages
such as increased bandwidth, load balancing, and high link availability. There are
two types of NIC bonding: switch independent and switch dependent.
NOTE:
Rebooting or reloading the QLogic FCoE driver (qlge), or adding other
network interface cards may change the value of the network ID.


















