Galaxy 65 User Guide
92
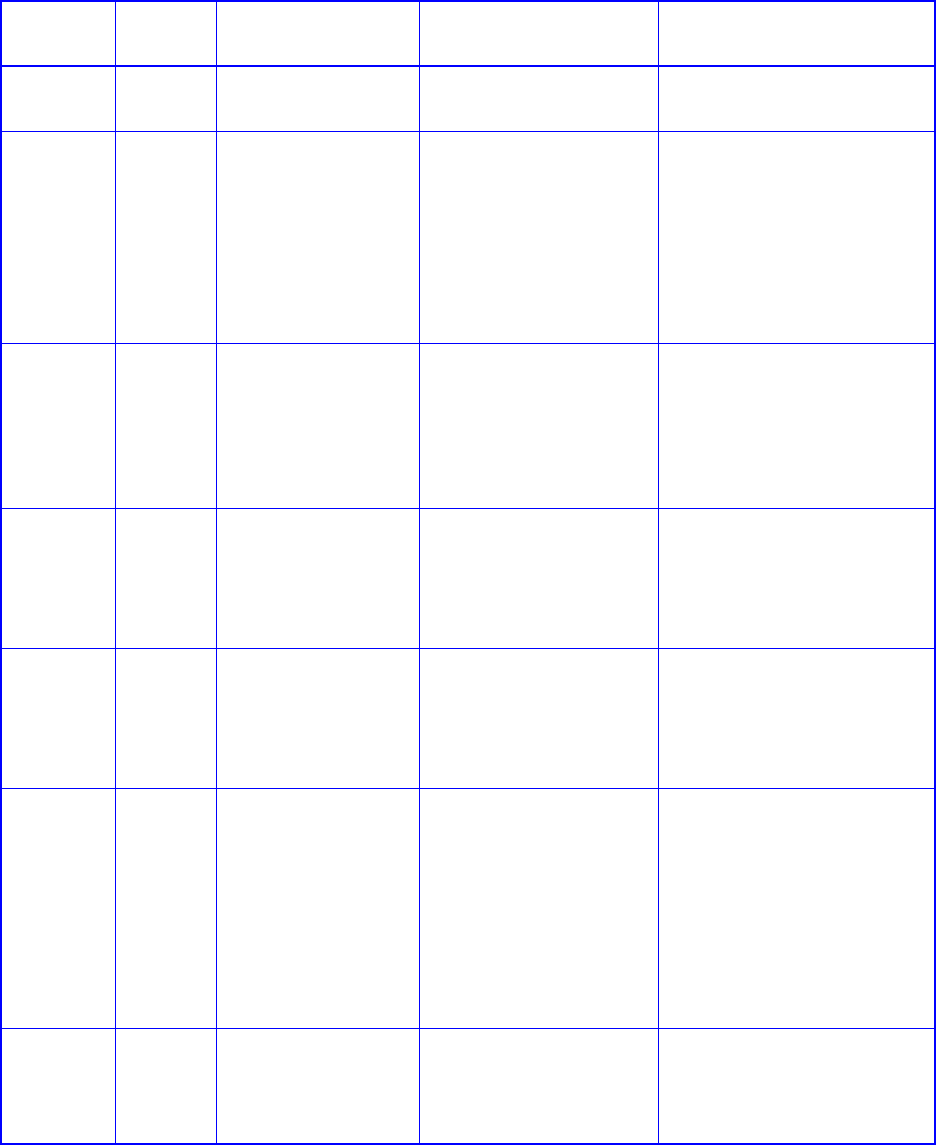
A.2 Comparing RAID Levels
Table 1–2 illustrates the differences between the different RAID levels.
Table 1–2 Comparing RAID levels
RAID Level Min No. of
Drives Description Strengths Weaknesses
RAID 0 2 Data striping without
redundancy
Highest performance No data protection—one drive
fails, all data is lost
RAID 1 2 Disk mirroring Very high:
Performance
Data protection
Minimal penalty on write
performance
High redundancy cost
overhead—because all data is
duplicated, twice the storage
capacity is required
RAID 2 N/A No practical use Previously used for RAM
error environments
correction (known as
Hamming Code) and in disk
drives before the use of
embedded error correction
No practical use—same
performance can be achieved by
RAID 3 at lower cost
RAID 3 3 Block-level data striping
with dedicated parity
drive
Excellent performance for
large, sequential data
requests
Not well-suited for transaction-
oriented network applications;
single parity drive does not
support multiple, concurrent write
requests
RAID 4 (Not
widely used)
3 Block-level data striping
with dedicated parity
drive
Data striping supports
multiple simultaneous read
requests
Write requests suffer from same
single parity-drive bottleneck as
RAID 3; RAID 5 offers equal data
protection and better
performance at same cost
RAID 5 3 Block-level data striping
with distributed parity
Best cost/performance for
transaction-oriented
networks; very high
performance and data
protection; supports multiple
simultaneous reads and
writes; can also be optimized
for large, sequential
requests
Write performance is slower than
RAID 0 or RAID 1
RAID 50 6 Combination of RAID 0
(data striping) and
RAID 5 with distributed
parity
Better random performance
and data protection than
RAID 5; supports more
drives than RAID 5
Lower storage capacity than
RAID 5


















