Managing Arrays & Partitions
115
You select a drive by highlighting it and pressing Enter. Each selected drive turns gray in the drive list.
After you press
Enter
for the number of drives you entered previously, the system automatically goes to
the next screen. To skip a drive, use the ↑ or ↓ key.
To toggle the display between the drive model number, serial number, and the node and WWN, press T.
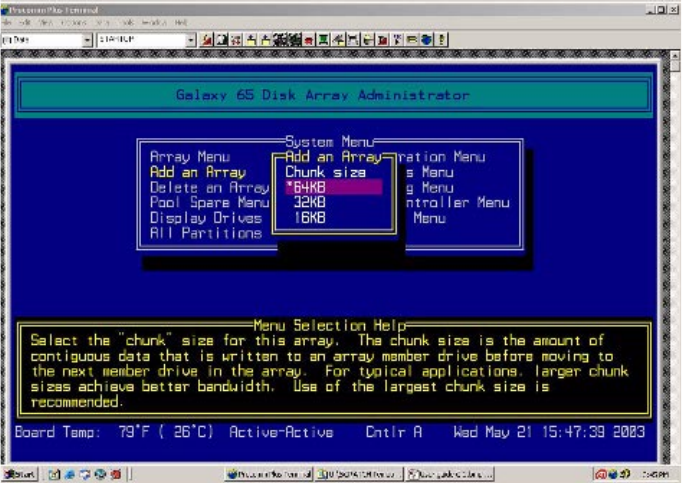
If the array you are creating is a RAID 3, RAID 4, RAID 5, RAID 10, or RAID 50, the Chunk Size screen
displays.
9 If the Chunk Size screen displays, select the chunk size and press Enter.
The chunk size is the amount of contiguous data that is written to an array member before moving to the
next member of the array. To determine the appropriate chunk size, refer to your operating system
documentation. For example, the default chunk size for Windows NT and many other operating systems
is 64 KB. If you are using the array for a database with very small records, you may want to use a smaller
chunk size.
If the array you are creating is a RAID 3, RAID 4, RAID 5, RAID 50, or Mirrored array, the Array Init
Options screen displays. The current option has an * next to it.
10 If the Array Init Options screen displays, select the option you want and press Enter.
• Offline Initialization: Using this option means you must wait for the array initialization process to
finish before using the array. It uses the zero method to create the array, which is faster than the
verify method.
•
Online Initialization
: Using this option lets you begin using the array immediately after creating it,
while the array initialization process runs. It uses the verify method to create the array, which takes
longer than the zero method.


















